Latest Blogs
IT Support
Ramsha Khan
Feb 12, 2026
What is an IT help desk? How will IT help Companies in 2026
Read More...

What is an IT help desk? How will IT help Companies in ...
In 2026, businesses are navigating a complex digital landscape. From cloud computing to AI-driven analytics, technology powers almost every aspect of operations. But as IT systems become more sophisticated, the need for reliable tech support grows. You can have an in-house IT team to handle everything, or you can have an outsourced IT help Desk team.
However, according to a LinkedIn study, the turnover rate of IT professionals in the software and technology industry has remained high at about 13.2% or higher for years. And if we’re talking about costs, just in the Northern US, a help desk agent remains in the office for about 2 years, but replacing them can cost around $12,000.
So, what are you to do in a position like this?
You can choose to go ‘the IT help desk outsourcing way’.
Not only is this a cost-effective solution, but a great partnership can go a long way, and both teams can benefit from it for years.
Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding what an IT help desk is? and how it can benefit your business is critical for staying competitive. Let’s explore the role of IT help desks, their key functions, and why outsourcing IT services is becoming the norm for companies worldwide.
An IT help desk is a centralized point of contact within an organization for resolving technology-related issues. Think of it as the “frontline” of IT support, handling everything from troubleshooting software problems to assisting employees with network access.
If we answer simply, what does an IT help desk do? We can say that it ensures that technology-related challenges don’t slow down business operations. A well-run IT helpdesk doesn’t just fix issues; it anticipates them, helping teams work efficiently and securely.
Some fundamental points about an IT help desk include:
By understanding the basics, companies can appreciate why an IT help desk is essential.
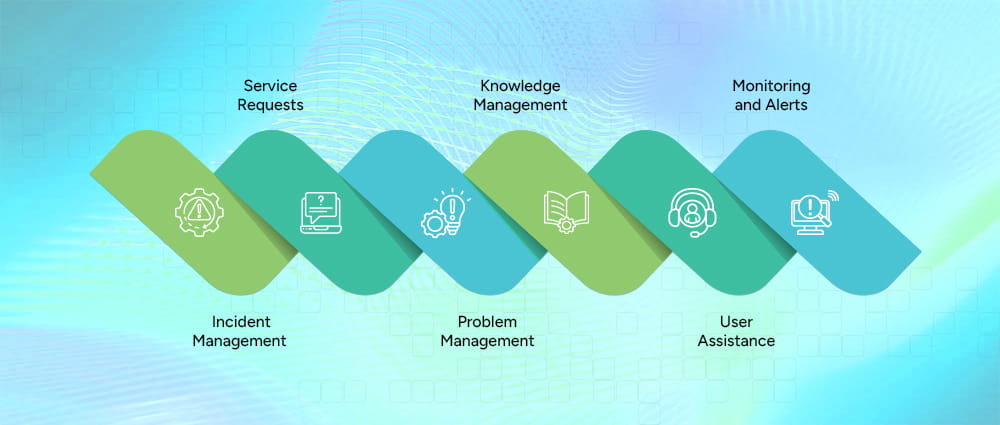
As mentioned above, an IT helpdesk is the central point of contact for all technology-related queries and issue resolution within an organization. The core functions of an IT help desk revolve around ensuring smooth IT operations.
Some of the main functions of an IT help desk are:
In the event of an incident, IT teams quickly identify and resolve user-reported issues to restore normal operations as fast as possible, reducing employee downtime and business disruptions.
There can be many employee requests for hardware or software. They send these service requests to the IT team, which manages everyday IT requests, including password resets, software installations, system access, and hardware upgrades, ensuring employees have what they need to work efficiently.
In this, your IT help desk services analyze recurring or complex issues to find the root cause and apply permanent fixes, helping prevent the same problems from happening again.
Through knowledge management, the team builds and maintains a centralized library of solutions, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides, enabling faster resolution of common issues in the future.
Like your customers need customer service, your employees, users, and team also require User Assistance. Your IT helpdesk service is primarily there for this function. They provide timely, real-time support via chat, email, or phone to guide users through technical issues and improve their overall experience.
Your IT service team continuously monitors systems, networks, and applications, sending alerts when potential issues arise so teams can act before failures impact users.
Essentially, an IT help desk fills the gap between technology and users, ensuring business operations stay uninterrupted.
Fundamentally speaking, an IT help desk software is a centralized platform that the IT team uses to manage, track, prioritize, and resolve technical issues reported by employees and users. Modern IT helpdesks rely heavily on specialized software to streamline support. Most IT help desk services use tools and software with the following features:
Efficiently log, track, and prioritize user issues from multiple channels such as email, chats, or web portals. Advanced ticketing systems can actually automatically categorize tickets, assign them to the right technician, and track progress until resolution, ensuring no request is lost or delayed.
AI-powered bots and workflows can handle repetitive tasks, such as password resets, software installations, and basic troubleshooting, freeing human agents to handle complex problems.
Allow users to solve common problems themselves through searchable knowledge bases, FAQs, and step-by-step guides. Self-service portals not only save IT staff time but also increase user satisfaction by providing instant solutions.
You can get easy-to-read reports showing things like how fast issues are being resolved, how many tickets are coming in, and any recurring problems. These insights help IT teams work smarter, improve performance, and fix issues before they become bigger problems.
Connect and work seamlessly with other business software, such as CRM or ERP systems, collaboration tools (Slack, Teams), and monitoring systems.
Provide technical support without physically being on-site, which is essential for distributed or remote teams. Remote access enables IT staff to troubleshoot devices, install updates, or fix configurations securely from anywhere, especially good for outsourced IT services.
Ensure secure handling of sensitive company data and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Features like role-based access, encryption, and audit logs protect information and maintain accountability.
Adapt workflows, ticket forms, dashboards, and automation rules to fit the organization’s needs. Scalable solutions grow with the business, supporting more users, devices, and complex processes as requirements evolve.
With these tools, companies can enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and deliver consistent IT help desk benefits to employees and customers alike.

Outsourcing IT support is no longer just a cost-saving tactic—it’s a strategic decision for companies aiming to scale and innovate. Here are six reasons why outsourced IT services will be crucial in 2026.
According to studies, IT helpdesk outsourcing has grown rapidly over the past few years, and the global market is expected to jump from around $10 billion in 2024 to $18.3 billion by 2033.
Help desk outsourcing is set to keep growing, with 91% of organizations planning to either maintain (56%) or increase (36%) the work they outsource. This means that the IT help desk outsourcing market has matured, making it easier for businesses to rely on proven external solutions instead of building in-house teams.
This convenience makes outsourcing a smart and attractive choice, and businesses are able to focus on core operations while ensuring seamless IT support.
Maintaining an internal IT team can be expensive due to salaries, training, and infrastructure costs, and well, the turnover rate mentioned above isn’t helping companies scale either.
Outsourcing to lower-cost regions like Asia and Latin America cuts both labor costs and the extra expenses of hiring, training, and keeping in-house staff. Plus, top providers offer flexible pricing, so companies can easily scale services up or down as needed.
Outsourcing IT help desk services allows businesses to convert fixed costs into flexible expenses. Companies pay for services as needed, optimizing budgets without compromising quality.
By 2026, AI and automation will play an even bigger role in IT support. Chatbots, predictive analytics, and AI-driven ticket routing help resolve issues quickly while enhancing the user experience.
One 2025 report by CallMiner CX Landscape found that almost all (96%) customer experience and contact center providers see using AI, including Generative and Agentic AI, as a crucial part of their success strategy.
Automated tools ensure that routine problems are addressed instantly, allowing human agents to focus on complex cases.
Outsourced IT help desk teams handle day-to-day issues, freeing internal IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives like software upgrades, network optimization, and cybersecurity.
However, most employees are quite frustrated with IT responses and prefer to solve their problems themselves. This means that IT services need quite a lot of improvement. This is one of the reasons why, in 2026, Managed IT services or IT service management (ITSM) is focusing on resolving issues faster and improving the overall user experience.
In this environment, companies are outsourcing their service desks to cut costs and deliver better support than they could in-house. Nearly 80% of organizations say their service is now better than when handled internally.
This improves overall IT help desk benefits, driving higher productivity across the organization.
Traditional Service Level Agreements (SLAs) focus on speed and resolution, but Experience Level Agreements (XLAs) prioritize user satisfaction.
Zendesk reports that 87% of IT leaders say experience-level agreements (XLAs) help them pinpoint areas where support can improve, with employee satisfaction being the top measure of service quality.
This is why outsourced IT helpdesk providers are increasingly adopting XLAs to ensure that employees feel supported, improving morale and efficiency.
Swarming support is a collaborative problem-solving approach where multiple experts tackle complex tickets simultaneously.
The traditional three-tier service desk, made up of generalists, technicians, and subject matter experts (SMEs), can slow things down for complex issues. Each handoff adds delays, increases costs, and reduces productivity. In fact, as tickets move up the levels, employee downtime can jump from 2 hours to an average of 9 hours and 28 minutes according to HappySignals.
Fast and efficient ticket handling is essential to keep employees happy and productive. That is why many help desk providers are turning to swarming for urgent or complex problems.
Swarming is a modern IT support approach where experts from different teams collaborate right from the start to solve issues quickly. It works especially well for time-sensitive or cross-functional problems, avoiding the delays and frustration that come with the traditional tiered model.
This method reduces resolution time and ensures higher success rates, giving businesses a competitive edge in fast-paced markets.

Several industries are adopting outsourced IT services to address unique challenges in 2026. Here’s a look:
The healthcare sector relies heavily on digital systems, from patient records to telemedicine platforms. Healthcare IT support ensures that hospitals and clinics maintain uptime, secure patient data, and provide uninterrupted care.
Outsourcing IT help desk services allows healthcare providers to focus on patient outcomes rather than tech issues.
Financial technology companies operate in highly regulated environments. Banking IT infrastructure and support for fintech platforms require precision, speed, and security.
Partnering with a fintech software development company offering IT help desk services ensures seamless transactions, cybersecurity, and minimal downtime.
Logistics operations depend on real-time tracking and system reliability. Logistics IT support ensures that shipments, inventory, and fleet management systems run smoothly, reducing operational bottlenecks and improving customer satisfaction.
Retailers are moving towards omnichannel experiences, which require constant IT support. Retail IT solutions and retail IT support help maintain e-commerce platforms, point-of-sale systems, and inventory management tools, ensuring a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Hotels and travel services are increasingly digital, using booking platforms, property management systems, and guest apps. Hospitality IT support ensures these systems function without interruption, enhancing guest satisfaction and operational efficiency.
As businesses evolve, partnering with the right IT helpdesk provider can make all the difference. Here, at Arpatech, we offer customized IT help desk services for each business we work with, designed specifically to meet the demands of 2026.
Two of the most important reasons why partnering with us can benefit your business for the better are:
Arpatech provides bespoke IT helpdesk solutions for businesses of all sizes. From SMEs to large enterprises, our team adapts support strategies to align with your goals, ensuring faster resolutions and improved efficiency.
With remote work becoming standard, Arpatech’s IT help desk for professional tech support ensures round-the-clock assistance, robust cybersecurity measures, and compliance with global standards. Businesses can rely on secure, efficient, and scalable IT support.
In 2026, the role of the IT help desk will be more critical than ever. Whether through outsourced IT services or in-house teams, companies that invest in reliable IT support will enjoy higher productivity, better user experience, and a competitive advantage in their industries.
By embracing automation, AI, and modern IT help desk software, businesses can resolve issues faster, reduce costs, and focus on innovation. Partnering with the IT Help Desk Support Services at Arpatech, you can ensure that your IT infrastructure remains robust, secure, and future-ready.
An IT help desk is no longer just a support function; it is a strategic tool for growth, efficiency, and operational resilience.
Choosing the right IT helpdesk service comes down to your company’s specific needs. At Arpatech, we recommend looking for a provider that offers:
A good IT help desk should not only fix problems fast but also help your team stay productive and satisfied.
While the terms are often used interchangeably, there is a difference:
Help Desk: Focuses on resolving technical issues like password resets, software problems, and hardware troubleshooting. It’s mostly reactive.
Service Desk: Offers a broader approach, including IT service management (ITSM), process improvements, and proactive support. It can handle incidents, service requests, change management, and reporting.
Many companies make these mistakes when setting up an IT helpdesk:
Arpatech helps companies avoid these pitfalls by providing easy-to-use platforms, optimized workflows, and actionable reporting from day one.
Internal Help Desk: Handles IT issues within your organization, supporting employees with devices, software, and network problems.
Technical Support: Can refer to broader support, including external customers, product troubleshooting, or specialized tech services.
Ramsha Khan
Feb 12, 2026
The 21 Best Telemedicine Software Providers for 2026: A...
Telemedicine has transformed the way healthcare is delivered around the world. Instead of driving to an office and sitting in a waiting room, patients now sit in the comfort of their homes and connect with healthcare providers online. From small clinics to large hospital networks, telemedicine software providers help healthcare teams reach more patients, increase practice efficiency, and improve health outcomes.
In fact, recent data shows that telemedicine usage rose significantly during the pandemic, with around 37 percent of adults reporting they used telehealth services in 2021, compared with just 11 percent in 2019. This dramatic rise shows how fast telemedicine has become part of routine care.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about telemedicine software in 2026: what it is, how it works, the core benefits, important features, how to implement it, challenges providers face, and the top 21 telemedicine platforms worth considering.
Telemedicine software is a special digital system that allows for the provision of medical care from a distance between patients and healthcare professionals. It combines all the tools necessary for secure communication, such as video appointments, electronic health records, messaging, scheduling, and billing, into a single solution.
Telemedicine software uses common technologies like:
These technologies work together to create a digital environment where care delivery is easier, faster, and more connected.
Telemedicine expands access to healthcare. Patients living in remote areas, those with mobility challenges, and busy individuals now have more ways to access care without travel. Virtual care can lead to better patient compliance and more frequent follow-ups.
Telehealth providers are also not left behind. When health operations go digital, we already know that patients benefit, but there are huge gains for the providers and hospital staff as well. These advantages include:
These benefits help both clinicians and patients have smoother, more satisfying experiences.
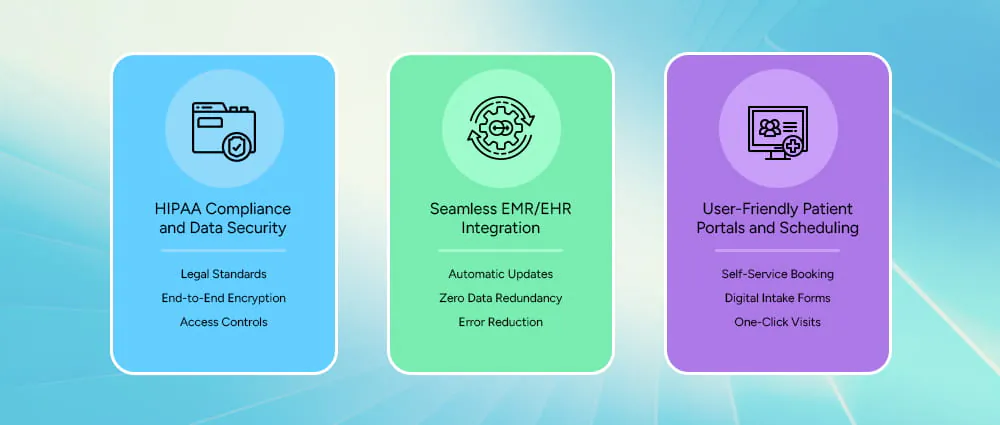
When you’re developing a Telemedicine app, there are a few mandatory healthcare-related requirements that must be included in the software, and we can’t skip them at any cost.
Telemedicine platforms must protect health data according to legal standards, including encryption and secure access controls. Providers must choose systems that meet privacy regulations to ensure patient trust.
Integrating telemedicine with EHR systems means that patient records update automatically. Providers don’t need to enter data twice, which reduces errors and improves efficiency.
Good telemedicine platforms let patients self-book appointments, complete intake forms online, pay bills, and join visits without technical headaches. This improves adoption and satisfaction.

Below are the Top 21 telemedicine software providers for 2026. Each review includes what makes the platform unique and how it helps healthcare providers.
Best for Large-Scale Enterprise Integration
Mend is a comprehensive telehealth solution designed for complex enterprises and large practices. It automates administrative tasks such as appointment reminders and patient registration.
This app uses predictive analytics to reduce no-shows and improve patient engagement with automated workflows. Providers can also customize the platform with branding and secure messaging to keep patients informed.
Best for Simple No-Download Access
Doxy.me is among the leading solutions for clinics looking for a simple yet effective telemedicine solution. Patients connect to the appointments via a browser link, thus no app installation is required.
The service offers video calls compliant with HIPAA, virtual waiting rooms, and basic integration with Electronic Health Records as features. Its user-friendliness is a perfect match for single doctors and small clinics.
The Industry Leader in Virtual Care
Teladoc Health belongs to the biggest telehealth software companies worldwide. It provides round-the-clock access to doctors for the different specialties like general medicine, mental health, dermatology, and chronic condition management.
The system has capabilities for advanced analytics, AI-driven risk assessment, and monitoring of patient outcomes. Its worldwide presence and ability to scale up make it suitable for very large hospital chains and telehealth operations at the enterprise level.
Best for Integrated EHR and Billing
athenaOne combines practice management, billing, EHR, and telemedicine into one unified system. Providers already using athenaOne benefit from seamless workflows without needing separate software. It supports scheduling, virtual visits, and billing within one shared environment, which reduces administrative burden and data duplication.
Used for Private Practitioners
SimplePractice is widely used by therapists, counselors, and solo healthcare providers. It combines telemedicine with practice management features like clinical notes, scheduling, billing, and insurance claims. Its focus on user experience and integrated tools helps small practices save time and manage all patient needs in one place.
Best for Patient Communication and Messaging
Klara is the one who offers the best communication tools for patients. Besides providing video calls, the company has secured its communication with messaging, reminders and patient engagement. The features of Klara lead to conversations among the three parties: doctors, staff and patients. The unified inbox of Klara diminishes phone calls and at the same time, increases the speed of replies.
The Software for Flexible Workflow Customization
eVisit is a provider of software for telemedicine that allows its users to customize the workflows to their liking. Among the extra features are virtual waiting rooms, advanced scheduling and support for complex cases in academic or multi-specialty practices. eVisit is flexible enough to keep up with the changes in the practice and even the growth.
Best for Remote Patient Monitoring
AMC Health is the company that specializes in remote patient monitoring (RPM) plus telehealth visits. They put patients’ wearable devices connected to provider’s dashboards that help doctors to monitor vital signs and even see the trends over time. This attribute is very effective in taking care of chronic patients like diabetics and those with heart diseases.
Best for Low-Bandwidth and Rural Areas
swyMed delivers reliable telemedicine performance even with limited internet speeds. It works in low-bandwidth environments, making it valuable for rural clinics and global health providers. It supports secure video, messaging, and device integrations.
Go for This if You Have Multi-Specialty Clinics
VCDoctor is a versatile telehealth system accommodating various specialties under a single umbrella. It encompasses online appointment setting, secure video conferencing, virtual waiting areas, and payment processing for patients. Clinics that offer varied services gain the most from their flexibility.
Ideal for Behavioral Health Experts
SecureVideo is the product of security and ease of use ceiling. It offers HIPAA-licensed video visits, secure messaging, and appointment tools. Psychologists and counselors, who work in the field of behavioral health, value its user-friendliness and privacy features.
The Most Secure Document Sharing and Faxing App
Updox is a powerful all-in-one communication platform built to simplify how healthcare teams talk to patients and share medical information. It supports secure telemedicine visits, encrypted messaging, eFax, and document sharing, all from one dashboard. This means doctors and staff no longer need to switch between multiple tools to send lab reports, prescriptions, or patient forms.
What makes Updox especially valuable is its ability to connect with over 100 EHR systems. This allows clinics to send and receive medical records directly from their existing software without printing, scanning, or manually uploading files. For busy practices, this saves time and reduces errors. Patients also benefit because they receive their test results and documents quickly and securely, which improves communication and trust.
Best for Collaborative Care
NextGen Virtual Visits is designed for healthcare teams that work together to treat patients. It allows doctors, nurses, specialists, and care coordinators to join virtual visits or share patient information in real time. This team-based approach helps ensure that everyone involved in a patient’s care stays on the same page.
The platform integrates virtual visits directly into clinical workflows, so providers can review patient records, write notes, and create treatment plans without leaving the system. Shared documentation makes it easier to coordinate care, especially for patients with complex or long-term conditions.
Best for Mental Health Practice Management
TheraNest is built specifically for therapists, counselors, and mental health clinics. It combines secure telemedicine with tools for scheduling, note-taking, billing, and client management. This allows mental health professionals to focus more on their clients instead of paperwork.
The platform also supports group therapy sessions, progress tracking, and outcome reporting. These features help therapists understand how their patients are improving over time and adjust treatment plans when needed.
Never Misplace Your Clinical Documentation
TherapyNotes is a favorite among counselors and mental health providers who want to keep their records organized and easy to access. It simplifies clinical documentation by offering structured templates for session notes, treatment plans, and progress reports.
It also includes secure telemedicine, online scheduling, and integrated billing, which means therapists can manage their entire practice from one system. With everything stored safely in one place, providers can spend less time on administration and more time caring for their patients.
Best for Behavioral Health EHR
Valant EHR Suite caters to behavioral health practices of all sizes. It includes powerful clinical documentation, scheduling, billing, and telemedicine features designed for psychiatric and therapy practices. Its data-rich dashboards help clinicians monitor outcomes and practice trends.
Best for High-Security Video Consultations
Healthie focuses specifically on secure, encrypted video sessions. Providers who want top-tier privacy for sensitive consultations, such as psychiatry or addiction medicine, find this platform especially useful. It supports virtual waiting rooms and secure file sharing.
The App for Specialized Medical Groups
Secure Telehealth delivers telemedicine tools tailored to specialized clinical groups. It offers customizable security settings, virtual visit templates, and clinical workflow support. Specialists who require specific documentation and visit types benefit from its custom features.
Best for Scaling HIPAA-compliant virtual care solutions
VSeeHealth is an adaptable telehealth and digital health platform that accelerates the development and expansion of virtual care systems in healthcare organizations. The platform provides secure HD video visits, remote monitoring, scheduling, and billing, among other things, thus being appropriate for hospitals, health systems, and specialty practices. The company has over 1,000 clients globally and processes more than 1.5 million HIPAA-compliant video encounters monthly, indicating its capacity to provide services at scale across urgent care, primary care, mental health, and intensive care.
Bring Discipline with This Healthcare Workforce Scheduling App
Deputy is focused on scheduling and workforce management for healthcare teams. While not a traditional telemedicine tool, it supports virtual care planning by ensuring providers are scheduled efficiently for online and in-person shifts.
Best for High-Definition Video Quality
BlueJeans Telehealth by Verizonprovides high-definition video conferencing optimized for medical consultations. It includes secure messaging, appointment reminders, and integration with scheduling systems. Its video quality makes it excellent for clinical assessments that require clear visual communication.
Providers use telemedicine for general appointments such as colds, follow-ups, wound checks, and medication reviews. Many chronic illness check-ins, like blood pressure and diabetes, can be done safely without in-person visits.
Telemedicine is also used for ongoing care of conditions like asthma, cardiac care, and postoperative monitoring. Remote monitoring tools share patient data with providers, allowing early intervention and better outcomes.

A Step-by-Step Guide to Telemedicine Software Solutions. This is what you’re going to need when you implement telehealth software features in your business.
In case your practice calls for one-of-a-kind workflows, superior integrations, or personalized branding, it would be wise to partner with a reputable telemedicine software development firm such as Arpatech.
Arpatech and similar companies develop telemedicine software solutions that are completely customized according to the client’s clinical and operational requirements, hence assuring seamless integration with EHR systems, patient portals, billing tools, as well as remote monitoring technologies.
This method provides health care professionals with more freedom, a better-growing along with a platform which suits their practical work processes rather than putting them into strict, off-the-shelf systems.
Providers must understand rules related to licensing, telehealth reimbursement, and data privacy in their region. Regulations vary between states and countries, making compliance complex.
Technical issues like poor internet connections, lack of patient technology skills, and device limitations can hinder telemedicine use. Providers must offer guidance and alternatives to improve access.
Selecting the right telemedicine software for providers depends on your goals, your patients, and how your practice works. Whether you need a basic video platform, a full EHR system, or a custom telemedicine solution, the platforms listed above are among the best options for 2026.
If you need something more personalized, Arpatech provides telemedicine software development services, including custom platform building, system integration, and ongoing technical support to help healthcare providers run virtual care smoothly.
Telehealth uses specialized systems like video conferencing, patient portals, EHR integrations, secure messaging, and remote monitoring tools designed specifically for healthcare.
Telemedicine software improves access, reduces wait times, enhances patient experience, and increases provider efficiency.
Telemedicine can provide urgent care, chronic disease management, therapy, follow-ups, behavioral health, and preventive medicine.
Patients need a device with a camera, internet access, and instructions on how to use the telemedicine platform.
By reducing administrative work, lowering no-show rates, and offering flexible scheduling, telemedicine helps practices serve more patients with less strain.
No. Providers must use secure, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine platforms designed for medical use to protect patient privacy and follow regulations.
Ramsha Khan
Jan 22, 2026
Telemedicine Startup Costs (2026): Factors Affecting th...
Telemedicine has become a critical part of modern healthcare, enabling patients to receive care remotely while giving healthcare providers tools to expand their reach efficiently. Whether it’s virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, or teletherapy sessions, telehealth is reshaping how care is delivered.
For entrepreneurs entering this field, the first question is often: What is the telemedicine startup cost in 2026?
Costs vary depending on technology, regulatory compliance, staffing, equipment, and marketing. Today, we will break down the factors affecting telemedicine startup costs, explain different platform options, and provide a roadmap for building a successful telehealth business.
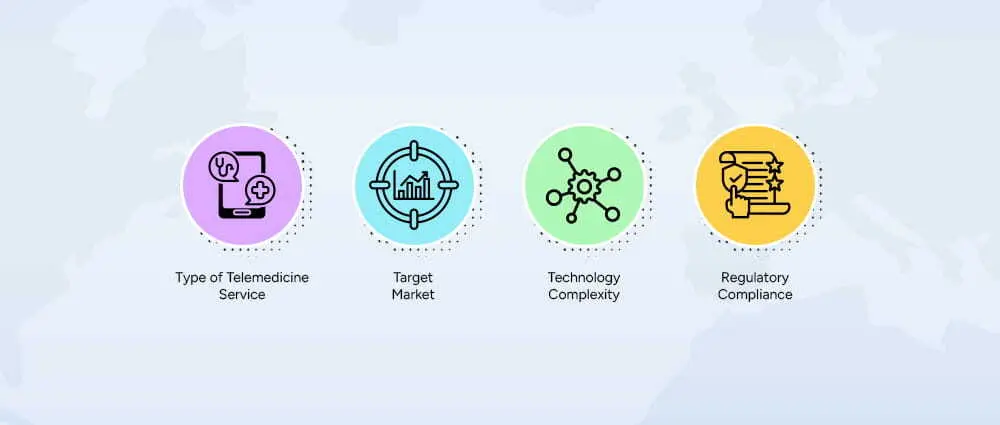
Even though we can say that a telemedicine startup cost can range from $8,000 to $150,000+, but if you’re looking for the breakdown, read ahead for that and learn what factors affect the costs. Telemedicine startup costs are not fixed. Several key factors determine how much your platform will cost:
The type of service that you provide will significantly affect costs. In the case of mental health therapy platforms, they will need to set up secure video consultations and also enact strict patient privacy measures, whereas, for chronic disease management, there will be a need for medical device integration and a more sophisticated analytics dashboard. The service’s degree of complexity will lead to increased telemedicine startup costs.
The budget is determined by the extent of your startup’s market. Providing services to a local clinic is much cheaper than targeting the whole country. A wider market is going to need more infrastructure, looser compliance, and most probably, a higher staff count.
Basic video consultation features, along with the patient chat option, are easy to build and cost around $15,000 – $50,000. On the other hand, next-generation solutions incorporating AI, remote patient monitoring, or multi-provider support can run up to $30,000 to $100,000+ or even more.
Healthcare is heavily regulated. In the US, HIPAA compliance and licensing are mandatory. Startups typically spend $5,000 – $15,000 on licensing and compliance. Skipping this step is risky and can lead to fines or legal issues.
Telemedicine platforms are not merely costly; they, along with the healthcare workers, save money too.
A smaller number of rooms is needed for the clinic, thus less rent and overhead.
Virtual consultations permit the doctors to have more patients at the same time, thereby lessening the monthly staff cost, which is between $3,000 – $25,000+, depending on the size of the team.
The automated processes of scheduling, reminders, and billing lead to a reduction in administrative costs.
Your telemedicine platform becomes more appealing to providers due to the cost savings it demonstrates, which leads to higher adoption rates and thus the long-term profitability of the providers.
Partnering with the right development team can make or break your startup.
Choose a telemedicine app development company that understands patient workflows and provider requirements.
The company should be familiar with HIPAA, state licensing, and other healthcare regulations.
A good development partner can start with an MVP and support future feature expansions.
Avoid hidden costs. Your partner should provide a clear breakdown of telemedicine app development services and related expenses.
A telemedicine startup is not just a technology project. It is a healthcare business, and healthcare leaves very little room for guesswork. A well-structured telehealth business development plan helps you avoid costly mistakes, control your telemedicine startup cost, and build a platform that can grow sustainably over time.
Think of this plan as your blueprint. It guides every major decision, from what features you build first to how much money you need to raise and how quickly you can scale.
The telehealth concept gets the examination of the market demand in the first place, and that is where the market analysis comes in. In order to develop the product, one must first have a clear picture of the user group and the specific issues that they want to solve.
The process includes understanding the patients’ behaviors, pinpointing the existing telehealth platforms’ weaknesses, and getting a grasp of the competitors’ strategies. This procedure is particularly crucial for new businesses planning to enter the US market, as patient expectations are high, and there are strict regulations over the quality of care.
During the market analysis the following aspects should be considered:
Well-executed market analysis means that your startup costs for telemedicine company in the U.S. or globally will be spent on the right solution, one that people indeed want and need.
A service model of your business will tell about the telemedicine startup in a way that it will make money. In fact, this decision will have a direct impact on both your revenue and long-term scalability.
The core question is whether the platform you would offer would serve patients, healthcare providers, or both. Each model has different operational and technical requirements.
The typical telemedicine service models are:
Choosing the right service model early on helps create features that align with revenue goals and also saves the cost of making changes later in the development process, which can be costly.
The technological roadmap of your platform indicates its evolution in the future. This particular method not only gives quicker launches but also better and more economical spending since everything will not be built at once.
At first, you should decide on your Minimum Viable Product, or MVP. Only the most critical features that can provide value are included here, such as video consultations, user onboarding, and appointment scheduling, etc. You will, later on, be able to add more advanced features gradually, depending on the user feedback, after the MVP is up and running.
A technology roadmap that is clear and precise usually contains the following:
The above-mentioned staggered method will help reduce costs related to the telemedicine app development, but at the same time, it will guarantee that the platform is flexible and ready for the future.
Financial projections summarize all aspects of the business scenario. It is in this section that you perform the calculation for the realistic cost of your telemedicine startup and the time needed to achieve the break-even point.
The projections must reflect not only the initial expenses but also the recurrent ones. Development, compliance, staffing, infrastructure, marketing, and equipment, among others, are included in this. The majority of startups fail to accurately calculate these costs, and if the budget is not controlled well, it can lead to significant financial problems.
Your financial road map should cover the areas of:
By indicating these costs explicitly, you will have an accurate estimation of the total cost of starting a telemedicine business and will be able to set funding or revenue milestones accordingly.
The business development plan for a telehealth company that is well structured and one that can adapt to any market, whether US or global, ensures that the budget for the telemedicine company is not based on pure guesses but on a well-thought-out strategy, market research, and the setting of clear priorities.
It not only enables you to maintain your attention, but also facilitates decision-making based on facts, and the development of a telemedicine platform that meets the requirements of being financially secure, ready for expansion, and compatible with the actual needs of the healthcare sector.
Telemedicine offers more than just software. One of the main factors involving telemedicine apps is the equipment:
Among hardware necessities are video conferencing devices, diagnostic tools, and networking equipment.
On the other hand are digital stethoscopes for tele-health, patient monitoring gadgets, and AI-assisted diagnostic tools.
The range of equipment costs is from $10,000 to more than $110,000 based on the complexity and scale of the establishment.
Opting for the right equipment provides the guarantee of patient safety and the effectiveness of service delivery at the least possible cost.
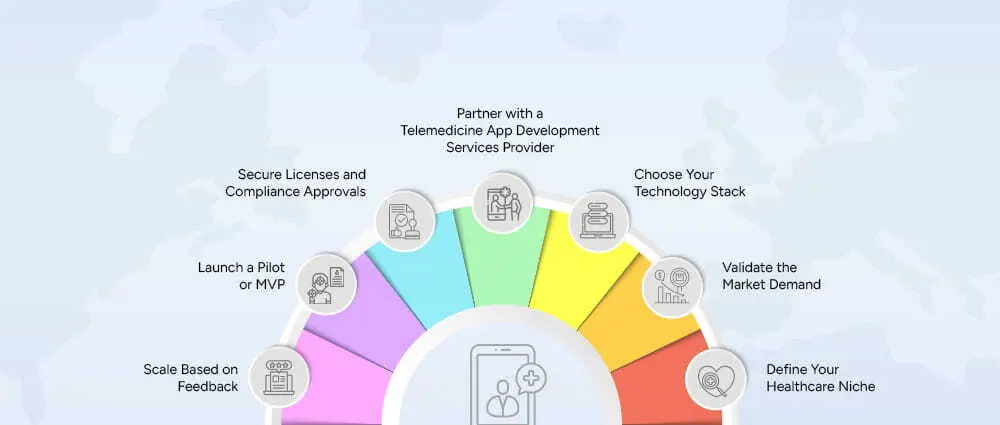
Establishing a telemedicine startup demands an organized plan. Every stage is highly important in managing the cost of your telemedicine startup and at the same time, setting up for future success.
The first thing that you need to do is to decide what kind of telemedicine service you are going to provide to your audience. Will the application focus on psychotherapy, general practitioners, ongoing illness treatment, or expert advice?
Narrowing down your niche will simplify your tasks like developing the product, coming up with a marketing plan, and even taking care of legal matters. A specific niche can cut down on costs that would otherwise be spent on uncovered features and services. The audience to whom these are directed is the one who needs them.
Before going the heavy investment route, check if there is demand for the niche you have selected. You may conduct surveys, interview potential users, and do competitor analysis.
Grasping the market is a way of ensuring that your medical costs for the US or global market are not wasted, thus the risk of developing a non-used platform is minimized.
The selection of your technology will impact your development costs alot. Therefore, it is essential to make a decision whether you need a mobile application, a web application, or both at this stage. Besides, you will have to go for the frameworks, databases, and cloud infrastructure that guarantee security and scalability.
Early selection of the right tech stack may help in eliminating rework with an accompanying cost and also ensuring your platform being able to cope with the entire growth.
A reliable partner for development will provide you with the expertise of medical workflows, safety measures, and complying with regulations. A telemedicine application development business can help you efficiently establish your platform while still assuring that it meets the legal standards.
Healthcare interoperability is a highly regulated industry. Securing licenses and complying with HIPAA or local regulations is mandatory. If you fail to meet these requirements, it can lead to legal penalties and project delays.
Usually, licensing and compliance can cost $5,000 – $15,000, but this investment safeguards your startup in the long term.
Instead of creating a comprehensive platform with all the functionalities at once, start with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), which includes the most important features like video consultations, patient registration, and scheduling.
The starting startup costs for telemedicine company US MVPs can go as low as $15,000 to $50,000 and at the same time, you can also test the market and collect user feedback without making a large expenditure.
Following the launch of your MVP, assess user activity and opinions to determine the order of improvements. Step by step, introduce sophisticated features like AI analytics, remote monitoring, or multi-provider support.
The process of scaling gradually makes sure that every investment is backed and it is less likely that you will build features that are expensive and not needed by the users. The cost of complex telemedicine solutions usually starts from $30,000 – $100,000+ as you scale up.
Each of these steps helps control your telemedicine startup cost by reducing uncertainty, avoiding rework, and ensuring your platform meets both market needs and compliance requirements. Following this roadmap sets the stage for a sustainable and successful telehealth business.
The true cost goes beyond development. Consider:
Accounting for these ensures you are not surprised by hidden expenses.
It is anticipated that overall spending on development projects will go up just a little in 2026 because the demand for sophisticated features will be on the rise as one of the main factors influencing this decision.

Most of the time, startups will start off with a white-label solution to validate their market, and then scale up their operations by switching to custom development later on.
To start smart:
This approach keeps your startup costs for telemedicine company US under control while building a sustainable business.
Launching a telemedicine startup in 2026 requires careful planning and budgeting. Understanding telemedicine startup costs, from development and staffing to equipment and compliance, helps you avoid surprises and maximize ROI.
At Arpatech, we specialize in creating custom telemedicine platforms that are secure, scalable, and fully compliant. Whether you need a basic MVP to test your market or an enterprise-level solution with advanced features, Arpatech’s telemedicine app development services can help you turn your vision into reality efficiently and cost-effectively.
When it comes to telemedicine startup in the US, it is mandatory to follow with HIPAA, state licensing, and patient data protection laws.
The price ranges from $8,000 through $150,000 or more, depending on the features, compliance, and staffing. Outsource the development or hire a telemedicine app development company, you will get about the same pricing.
Telemedicine is profitable through subscription fees, per-consultation charges, and B2B collaborations. Besides, reduction in operational costs for doctors makes it easier for them to switch over to telemedicine.
The charges depend on platform complexity, session volume, and staffing. Teletherapy necessitates a secure video infrastructure and compliance measures.
Telemedicine is not just an issue of accessibility, convenience, and cost but a very strong rotating business opportunity with a growing demand factor.
Ramsha Khan
Jan 8, 2026

Telemedicine App Development from Scratch – Guide...
Telemedicine has come a long way, and it is no longer just a convenient video call to the rehabilitation doctor. By 2026, it had developed to become a major staple of contemporary health care. Fast consulting, remote monitoring, digital prescriptions, and seamless communication with medical professionals are some of the things that patients are now expecting and that is why more and more hospitals, clinics, and health care startups are pouring their resources into telemedicine apps. Patients no longer have to visit the provider in person; they just go where there is digital access.
The need for trustworthy and safe telehealth platforms has led to organizations hunting for the best telemedicine app development company. But here is the bright side. The creation of a telemedicine application from scratch is fully doable, even if you’re not a techie. What you need is only a well-defined strategy, appropriate tools, and a clear roadmap.
Today, here we will guide you through the entire process, starting from the understanding of the telemedicine market in 2026 to the telemedicine app development, what features it should have, and the trends your app should be following.
Telemedicine is no longer a niche convenience service. It is rapidly becoming a foundational component of global healthcare. As we look toward 2026, the scale, reach, and expectations for digital health platforms have grown dramatically. The market data from 2023–2025 point to a strong and accelerating adoption across regions, settings, and specialties.
In short, this data above clearly shows an expanding and accelerating market.
Because of this growth, more institutions are investing in, custom telemedicine app development solutions to future-proof their services and offer digital health at scale.
Multiple factors contribute to the boom in telemedicine. The data and broader industry shifts help explain why demand for telemedicine apps and services is skyrocketing:
The boom in telemedicine can be attributed to multiple factors. The data and wider industry transitions are helpful in explaining the increase in the demand for telemedicine applications and services in the following ways:
The global elderly population, rise in chronic diseases, and absence of adequate medical professionals in remote or sparsely populated areas have all contributed to the need for healthcare systems to be remote and accessible.
Patients like to have the option to choose: they can have remote consultations, less travel or waiting time, and better follow-ups. This has facilitated the transition of many providers to the digital-first model. Telehealth contributes to a reduction in hospital readmissions and emergency visits, hence creating a win-win situation for both patients and providers.
Better internet access, widespread smartphone usage, wearables, and infrastructure improvements are making remote monitoring, data sharing, and digital consultations more dependable. The above-mentioned improvements have empowered the healthcare organizations to take the risk of investing in telemedicine mobile app development solutions.
There is a greater focus on preventive care and remote monitoring (especially for chronic disease patients). Now, patients don’t have to go to the hospital for every check-up; they can just have a telemedicine consultation and get care at home. This shift pushes the use of remote patient monitoring together with virtual consultations.
More and more hospitals and healthcare providers are now seeing telehealth not as a temporary solution but as a permanent strategic option. They are making investments in establishing or joining forces with others to create comprehensive telemedicine ecosystems.
With the success of telemedicine, the governments and regulatory bodies in different parts of the world have started to set up the necessary conditions for digital health services. This not only increases trust and compliance but also diminishes the obstacles for healthcare organizations to put in place remote care solutions and thus, the demand for full-fledged edge computing telemedicine app development services is rising sharply.
Healthcare organizations are increasingly inclined toward custom telemedicine app development, which is secure, scalable, integrated and tailored to meet their specific needs rather than towards one-size-fits-all generic solutions.
From the perspective of market dynamics, generic or off-the-shelf telehealth platforms usually do not meet the needs of the organizations. This is the reason why custom-built solutions are widely chosen:
All these factors put together provide an explanation for the strong demand for and the high supply of telemedicine app development services, and for the trend of many healthcare providers to collaborate with experienced development firms instead of sticking to generic products.
The telemedicine industry in 2026 is shaped by both technology and patient expectations. Here are the top trends influencing the future of telehealth platforms.
AI has reached the point where it is the main character in all the healthcare digital transformation stories, from smart symptom checking to clinical decision support, appointment routing, and predictive analysis. To put it simply, AI triage apps have turned doctors into less busy but more efficient healthcare providers as they get patient answers in no time.
Telemedicine applications work hand in hand with smartwatches, glucose monitors, ECG devices, and fitness bands that cut each other’s waiting time. As a result, monitoring of chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension can be done remotely.
Certain medical areas are utilizing VR in rehabilitation, mental health, and physical therapy. VR provides engrossing treatment sessions, making therapy more effective and at the same time more reachable.
Patients count on the applications to keep track of their medical history, habits, medication timings as well as preferences. Bespoke dashboards not only enhance but also engage and keep the patients.
The benefits of telemedicine apps include automatic system prescription updates, reminders, and pharmacy delivery services.
Rather than developing separate video call applications, healthcare companies nowadays prefer investing in entire systems. Such systems comprise patient portals, doctor dashboards, admin control panels, and integrated billing.
These trends indicate why organizations lean towards custom telemedicine app development rather than opting for off-the-shelf software. A custom approach gives total control over the features, the user experience, and the compliance.
Telemedicine is not just for general checkups. It has expanded into nearly every area of healthcare with practical, high-impact use cases.
Patients have the opportunity to consult with doctors at any time, without the need to travel or deal with congestion in hospitals.
Mobile applications follow up and monitor chronic diseases like diabetes, asthma, and heart disease. Physicians keep an eye on the patients’ health data and make changes to treatment plans from afar.
Internet-based counseling, therapy, and psychology consultations are not only frequently used but also very effective.
Prescription medicines are stored electronically, renewal process is simple, and delivery to pharmacies is done automatically.
Patients in underserved regions get access to specialists that are not available locally.
Patients are able to send recovery photos, vital signs, and symptoms to the medical staff via the application instead of going for several hospital visits.
Telehealth with the support of AI is helpful in the evaluation of emergency cases and the redirection of patients to instant care.
Telehealth services provide safe and easy-to-do consultations for young children and seniors who cannot leave their homes due to health issues.
Healthcare providers that implement such models usually search for a telemedicine application development that offers a good user experience along with strong compliance and efficient real-time data management.
If you are planning to build a telemedicine app from scratch, following a clear step-by-step approach makes the entire journey easier.
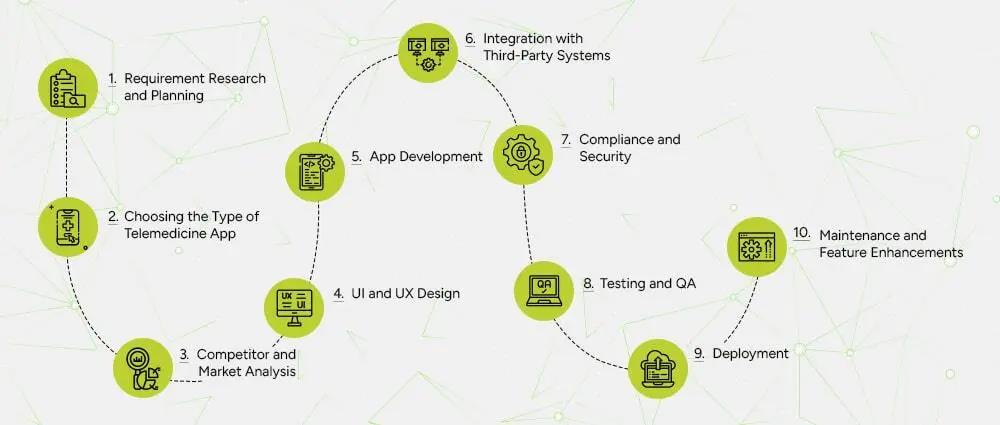
Telemedicine users want clarity. Good design keeps them engaged and confident.
The real coding action starts here. Developers create:
This phase often needs a skilled telemedicine application development company.
Compliance is critical in telemedicine. Developers ensure:
Security is a non-negotiable part of every custom telemedicine app development solution.
Test for:
Launch your app to the Apple App Store, Google Play Store, or your organization’s private environment, depending on your target audience.
Maintenance and on-going support includes:
A long-term partnership with a reliable telemedicine app development service ensures your app continues to grow with your business.
To succeed in 2026, every telemedicine app must include a strong set of essential features that support smooth communication, secure data handling and reliable patient care.
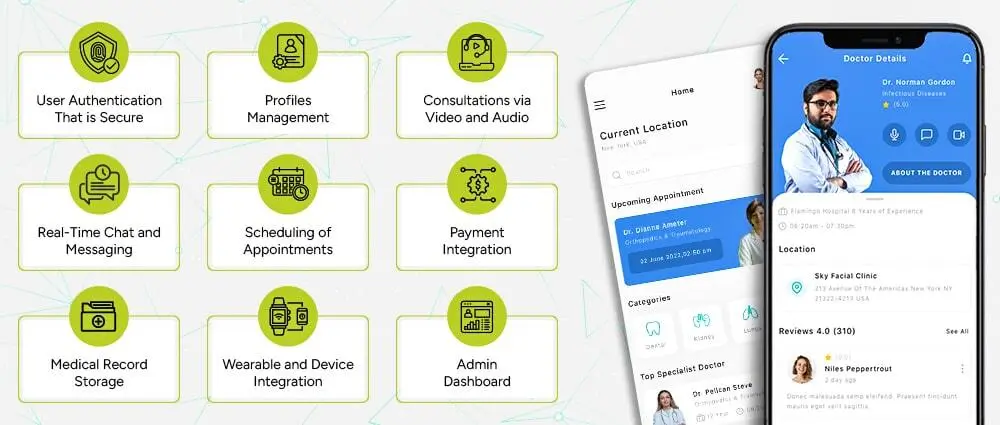
Provide login through email, phone number, and two-factor confirmation, so that only the authorized people to access medical information can be there.
Make it possible for patients, doctors, and admins to create comprehensive profiles that keep the major facts and make the diagnosis more precise.
Offer very good and clear communication in terms of video and voice because virtual appointments are very much dependent on stable and clear connections.
Facilitate secure text messaging for the purpose of making patients asking follow-up questions and sharing reports or images, for instance, file sharing.
Allow the users to book, reschedule, or cancel appointments without any problem while doctors are controlling their availability in real-time.
Support smooth and secure online payments for consultations, follow ups and treatment plans.
Store reports, images, previous consultation notes and health history in encrypted formats for easy future access.
Connect with smartwatches, glucometers and other devices to capture live patient data for better diagnosis.
With healthcare IT support, give administrators tools to manage users, doctors, reports, billing, support tickets and system analytics in one place.
Companies that build all these elements into their apps usually offer a wide range of telemedicine app development solutions that meet modern healthcare needs.
The cost of telemedicine app development is based on several factors like features, the type of app, technology used, and the place where it is done. Even though all projects differ, below is a rough estimate.
This is where companies usually invest in custom telemedicine app development for long term scalability.
Cost also depends on whether you choose:
Telemedicine has completely changed the entire healthcare interoperability experience by increasing accessibility, speed, and efficiency of medical support.
As we step into the year 2026, every healthcare provider that wishes to remain competitive must undergo a digital transformation. This is the reason why telemedicine app development process is emerging as a high-growth area in healthcare technology.
Building your telemedicine platform is a way to growth, better patient engagement, and stronger service delivery irrespective of whether you are running a clinic, managing a hospital network, or creating a healthcare startup. Besides, the telemedicine app development company, a good plan, and user experience will help create a trustworthy digital healthcare ecosystem that is audience-tailored.
Each phase from market trend comprehension to needed features selection, following telemedicine app development process, modern technologies addition, security assurance, etc., is a contributor to a successful launch. Custom solutions that allow designing workflows, interfaces, and connections really match your medical operation are particularly diversified.
Digital is the future of healthcare and telemedicine is at the forefront of it. So, work with Arpatech to give your telemedicine shape and create a solution for your patients that helps them to the maximum.
The telemedicine software spectrum is quite vast comprising different types of applications based on the requirement, from very basic video consultation platforms to sophisticated health record and remote monitoring systems. The most common software parts are:
If you choose to work on a custom telemedicine solution, the entire software components are integrated to provide a secure, flexible, and scalable telemedicine experience.
Yes, AI and other associated technologies have become a major factor in the development of modern telemedicine. The use of AI in telemedicine apps is not uncommon. Here are some of the activities that AI performs in this field:
Thus, AI is not simply something you can say is nice-to-have; in fact, it is the core part of the solution in the case of multiple advanced telemedicine app development, where it helps to improve efficiency, accuracy, and patient experience.
Remote consultation, which allows to see, hear, or chat with the doctor, is the most common type of telemedicine, and this type is without a doubt the most preferred among all doctor-patient consultations, which makes it the main scenario in telemedicine.
Nonetheless, there are also other consultations supported by telemedicine like remote monitoring of the patient, managing diseases, e-prescriptions, and mental health consultations, etc.
Though physicians’ consultation via telemedicine is the most common and the simplest form of it, yet telemedicine is wide-ranging and continues to be the impenetrable barrier of accessing healthcare for a lot of providers that have already gone digital.
Choosing the best telemedicine app or development solution depends on your needs and priorities. Here are key factors to guide you:
Selecting a telemedicine app development company’s solution that balances all these factors will make your telemedicine app reliable, user-friendly, and future-proof.
The implementation or utilization of telehealth apps has numerous advantages for physicians and medical practitioners:
This is actually a matter of who your target users are and what are their scenarios. The following is a decision guide that is very simple:
To put it simply: there is no one-size-fits-all solution. You can say that the best platform is determined by your user base, budget, required features and long-term vision.
To build modern telemedicine applications, the following are the technologies that top the list:
These technologies, when combined properly, allow building a robust, secure, and feature-rich telemedicine mobile app development solution.
Ramsha Khan
Dec 25, 2025

Enterprise Software Development for Healthcare: Using A...
Healthcare is moving into a new era where patients expect fast digital services, hospitals need stronger data security, and administrators want systems that actually make their jobs easier. With so much pressure to upgrade, one thing has become clear. Legacy systems can no longer keep up. The future belongs to digital platforms that integrate smoothly, scale easily, and support automation.
This is where Healthcare Software Development Services and enterprise software development services come into play. Application Modernization Services that rebuild old legacy systems into cloud-native solutions are no longer optional. It is essential for better patient outcomes and smoother hospital operations.
Here, we’re going to explain what is changing in the healthcare industry, why modernization is necessary, and how hospitals can transition to secure, cloud-based, AI-enabled systems by 2026 and offer better healthcare for a long time with no data or power outages for a long long time.
So, let’s learn about the challenges that these legacy systems are burdening the healthcare industry with right now, and how bringing in a cloud-based native system can change it all:
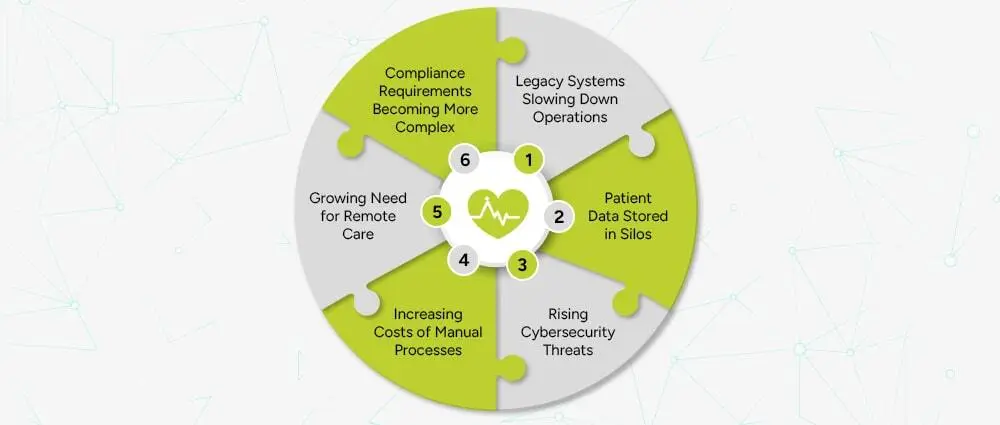
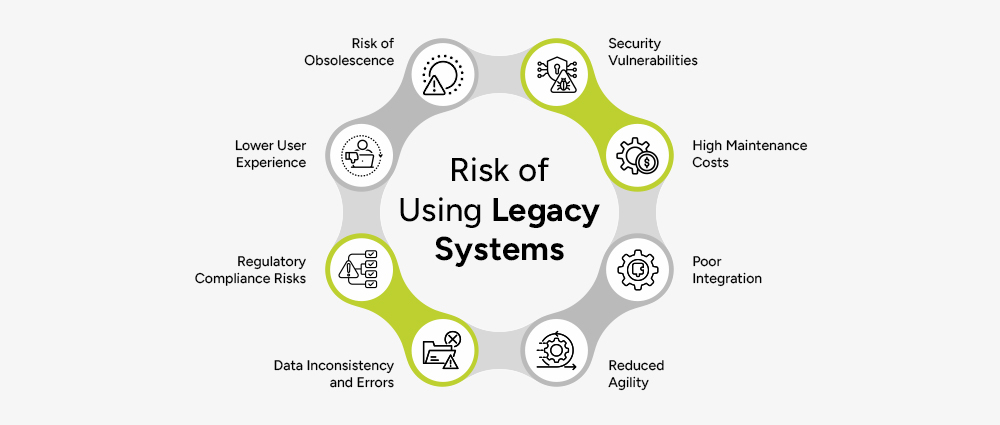
Healthcare organizations across the world face several challenges. Many of these problems come from outdated technology, slow systems, and disconnected software platforms.
Many hospitals still use systems built 10 to 20 years ago. These legacy platforms create problems such as:
These issues affect doctors, nurses, administrators, and patients alike, which is why it is necessary to employ legacy application modernization strategies within our systems.
Patient information is often divided across multiple systems. The lab has its own records. The pharmacy uses separate software. Insurance claims run on a third system. This creates delays, errors, and miscommunication.
Healthcare is among the most attacked sectors globally in cybersecurity. Ransomware assaults, data leaks, and downtime of systems are sources of financial and legal risks. Outdated systems are the easiest to attack.
Manual work is a necessary component in tasks like billing, scheduling, insurance checking, following up with patients, and keeping track of inventory. The burden can be lessened through automation, but older systems do not have the capability to work with the new automation tools.
Telehealth, virtual consultations, and cloud-based patient monitoring grew after the pandemic. Many hospitals still lack systems that support remote services effectively.
Healthcare organizations must follow strict standards like HIPAA, GDPR, local authority rules, and insurance reporting requirements. Outdated systems often lack built-in compliance support.
All of these issues point to the same solution. Healthcare institutions need Custom Software Development, cloud solutions, application modernization services, and modern enterprise software platforms that can meet the demands of 2026 and beyond.
Enterprise software development services are designed to help hospitals move from outdated platforms to smart, scalable, and fully integrated systems. With the right Healthcare Software Development Company, healthcare organizations can build custom software development solutions that support their exact workflows.
Hospitals depend on many systems. Cloud application modernization does not mean replacing everything. It means upgrading or rebuilding these systems into a connected cloud ecosystem.
Let’s break down the core healthcare systems that are commonly used in hospitals today, and how they can be modernized.
Hospitals require a complete management solution that handles:
Legacy HMS platforms often lack automation and advanced analytics. Modern application modernization services and enterprise solutions include cloud native architecture, mobile access, and smart dashboards.
A PMS, Patient Management System, also known as Patient Portal, manages individual patient records, history, medications, and reports. Older PMS systems are slow and disconnected. Today’s application modernization services offer:
Hospital ERP systems manage:
Modern ERP solutions improve cost control through:
Insurance processes are often manual. Healthcare Software Development Services can create custom insurance claim apps that enable:
Hospitals are rapidly adopting telemedicine. With custom software application development, hospitals can integrate:
An LIMS systems created using application modernization services help labs automate:
A pharmacy system currently made using application modernization services supports:
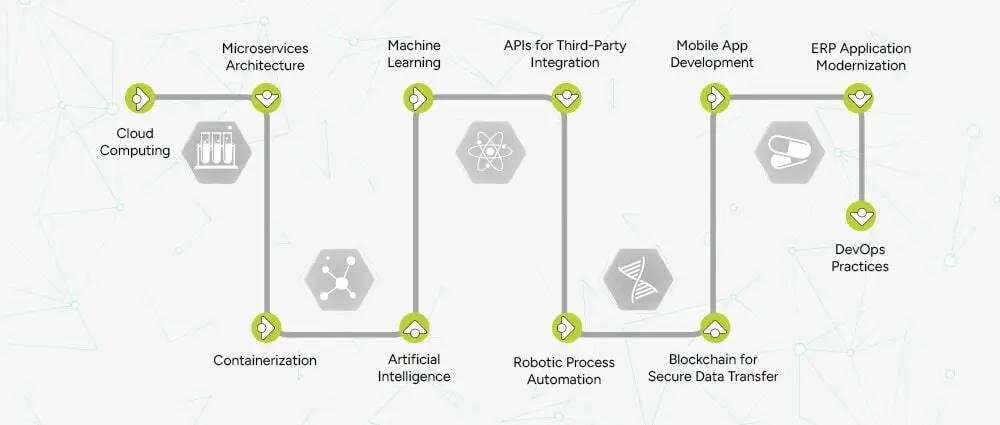
To modernize these systems, healthcare organizations can rely on several technologies offered through Custom Software Development Services. Key technologies include:
Cloud computing is a big step forward for hospitals. They get rid of their old servers and can keep their data securely in the cloud. The systems are therefore faster, easier, and are accessible from anywhere you like.
Microservices help large hospital systems get divided into smaller parts, which can then be updated or fixed without interrupting the entire thing. This way, hospitals can scale faster and ensure better performance.
Containerization packages apps in a way that enables them to run flawlessly on any device or environment. With the help of application modernization services, in return, it allows development teams to quickly release updates with fewer errors.
AI serves as a helpful tool for hospitals by making data analysis, decision-making, and doctor-assistive tools easier and smarter. By providing faster insights, it not only reduces mistakes but also improves medical treatment.
In application modernization services, machine learning gives power to software programs to learn from past data and improve and become smarter over time. Hospitals can use it to predict patient care, identify high-risk groups early, and cut down on the time it takes for diagnosis.
APIs help different healthcare systems talk to each other easily. Through them, hospitals can link laboratories, pharmacy systems, insurance platforms, and patient applications without the necessity of manual work.
RPA is a technology that takes care of the repetitive administrative tasks of the organization, allowing staff to devote more time to patient care. It is particularly suitable for activities like billing, scheduling, claim processing, and data entry. So, add RPA into application modernization services and get rid of manual work for a long time.
The use of blockchain in the healthcare industry is there to ensure that medical data files are shared safely between parties and are not tampered with. This is the foundation that builds trust between hospitals, insurance companies, and patients.
Mobile apps are the main source through which doctors, nurses, and patients can get instant access to important information. Hospitals can provide telemedicine, appointment booking, and easily get patient record access to their clients via cell phones.
Modern ERPs help hospitals manage finance, HR management, procurement, and operations more efficiently, all in one place. ERP application Modernization services and systems of integrated networks offer real-time insights that help reduce costs and improve planning.
DevOps practices are the base that enable development teams to deliver updates faster without system downtime. This makes sure that hospital software stays stable, secure, and up to date at all times.
Each technology helps hospitals reduce costs and increase efficiency.
One of the biggest steps in application modernization services is cloud adoption. By moving systems to the cloud, hospitals gain flexibility, speed, and stronger security.
Healthcare Software Development Services often include the following cloud solutions.
Cloud Migration involves moving existing systems to cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Cloud migration offers:
Instead of simply migrating old systems, hospitals can build entirely new cloud native apps that support:
DevOps in application modernization services helps hospitals release updates faster and maintain systems without downtime. DevOps engineers support:
DevOps combined with cloud technology improves patient services and lowers maintenance costs.
Healthcare data is highly sensitive. Cloud-based systems require strict compliance. A reliable Healthcare Software Development Company offers:
Healthcare systems cannot afford downtime. When offering application modernization services, reliable providers offer:
Ongoing support ensures that healthcare teams remain productive around the clock.
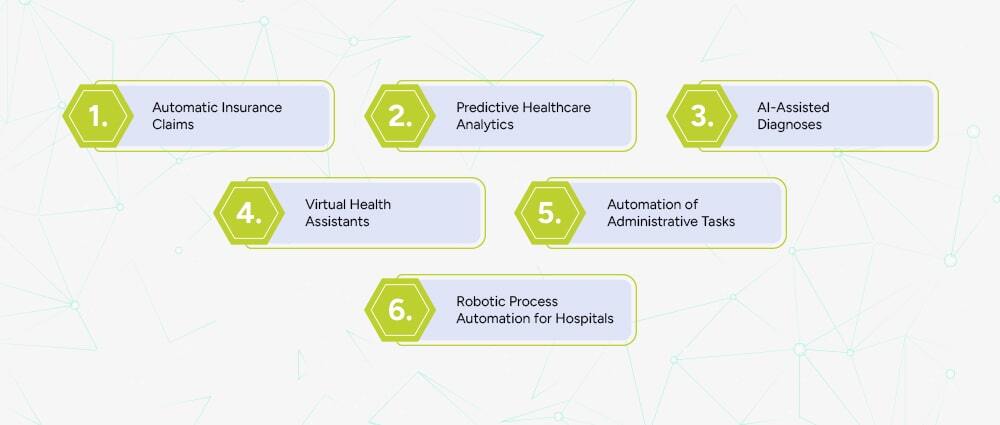
Artificial intelligence and automation are transforming the healthcare industry faster than ever before. By 2026, AI-driven systems will be an essential part of healthcare operations.
Below are some of the latest advancements.
AI can read claim documents, verify details, detect errors, and submit claims automatically. This reduces delays and increases approval rates.
AI in application modernization services can analyze large datasets to predict:
Predictive analytics helps hospitals prepare in advance.
By using AI in application modernization services and following AI software development companies that are building tools that support doctors by analyzing:
These tools help identify diseases early and reduce human error.
Chatbots and virtual assistants can help patients with:
By enabling application modernization services in thier systems, hospitals can automate:
Automation reduces the burden on staff and improves patient satisfaction.
RPA is being used to automate repetitive tasks inside hospital systems, including:
These technologies make healthcare operations faster and more cost-effective.
Choosing the right Healthcare Software Development Company is the most important decision for modernizing systems. Hospitals must assess expertise, security practices, technology stack, and long-term support capabilities.
Here are some factors to consider.
Pick a company that has experience in:
Your partner should be able to upgrade or create:
Advisory services are important because they help hospitals understand:
Hospitals have unique workflows. Your partner must offer:
By choosing Offshore Software Development Services or Nearshore Software Development, hospitals can reduce development costs while working with skilled experts.
Offshore Software Development also provides access to larger talent pools.
When you are outsourcing software development, you must ensure your partner provides:
Your partner must understand:
Arpatech offers healthcare organizations a complete range of Application Modernization Services and enterprise software development services. Hospitals can rely on Arpatech to modernize their legacy systems and build cloud native apps for 2026.
Arpatech supports businesses that want to:
This allows hospitals to reduce costs while receiving high-quality development.
Fast, secure, cloud-based, and AI-enabled systems will be the ones that define the future of the healthcare industry. If hospitals want to compete, they have to give up on old-fashioned platforms and provide first-rate care to patients.
Taking advantage of Healthcare Software Development Services, modern enterprise software development practices, and cloud native infrastructure, healthcare organizations will be able to build an excellent digital foundation for 2026 and the years to come.
website
Modernization of applications is not solely about technology shift. It is a move towards the direction of better treatment to patients, more efficient operations, less expenditure, and sustained victory.
If you require assistance in reshaping your medical systems, then firms such as Arpatech can supply you with the experience, technology, and support that will lead you from the status quo of old systems to the transformation of native cloud application modernization healthcare platforms.
Let’s work on your Healthcare system today!
App modernization is the way of turning an old application into a new one by upgrading it really fast, making it very secure, and adapting it to new technology. The app can choose from a range of options such as moving to a new location, getting extra features, or even a better user interface.
Legacy systems in healthcare signify the long-used technologies that hospitals still depend on even if they do not meet the current requirements. Most of the time, these systems function slowly and do not have the capability to interact with and work along with the new applications.
A large variety of digital tools are available in healthcare, each fulfilling a certain need. The most common types include:
All these tools combined make it possible for hospitals to operate more efficiently and provide better care.
There are several reasons why application modernization is necessary:
Not modernizing might mean that companies lose their competitive edge and suffer from poor customer service.
Application modernization is typically done in a step-by-step manner:
Following these steps will enable companies to upgrade their applications without affecting their everyday operations and will be done in a timely manner.
Cloud application modernization means moving existing applications to cloud infrastructure while updating them to take full advantage of cloud features. This allows apps to scale easily, run faster, and be accessed from anywhere. It also improves security and reduces the cost of maintaining physical servers.
Ramsha Khan
Dec 11, 2025
Enterprise Application Development: A Complete Guide fo...
If you’re sitting in the C-suite, you already know this: the business landscape in 2026 demands agility, integration, and relentless efficiency. It’s no longer enough to patch together legacy systems and hope they talk to each other.
What is required is a full-scale strategy for Enterprise Application Development Services, which forms the basis of your business operations, innovations, and growth.
Let’s investigate the perspective that modern enterprises should have towards the implementation, deployment, and development of enterprise applications. It does not matter whether your focus is on core software, mobile applications, web applications, cloud integration, or a combination of all of them. We are working towards shifting the narrative from: We should build an app. To: We have a full enterprise app ecosystem powering everything.
By the end, you’ll not only understand what needs to happen, but how to act, so you can brief your team or vendor and execute with confidence.
However, if you’re new to the app development sphere, here’s what an enterprise system is and how it can help your business scale like never before:
Enterprise Application Development is the method through which the large-scale software systems get designed, built, and deployed that link an organization as one united digital ecosystem across various departments, regions, and business units.
In contrast to consumer applications that are limited to a single function or user group, enterprise apps are constructed in such a way that they can cope with intricate workflows, large amounts of data, and different security levels and access rights. They integrate the whole HR, finance, operations, supply chain, and customer management departments on one platform, which enables data sharing and decision-making to be done in real-time.
Why do you, as a large organization, invest in enterprise application development in the first place? Obviously, it’s due to the old models of siloed departmental systems, manual data transfers, fractured user experiences, and disconnected mobile/web capabilities that are no longer acceptable. Let’s break the problem down:
You’re not a single-user startup. You serve hundreds or thousands of employees across multiple geographies and business units, including HR, procurement, supply chain, finance, and operations. Yet your software still acts like it was built for only 10 users. That conflict creates inefficiencies.
Your departmental tools are unable to communicate. HR has its own platform, procurement uses spreadsheets or manual solutions, supply chain and inventory systems are legacy, maybe on-premise.
What do these issues result in?
Mobile and web demands are blowing up. Your workforce is remote, hybrid, and international. They expect mobile access, web portals, dashboards, and real-time data. If your enterprise software doesn’t keep up, you suffer productivity losses and user frustration.
Cloud, SaaS, mobile, and security are all converging. If you build only web or mobile systems for specific departments, you risk being outdated. You need an ecosystem approach.
From a business standpoint, operations, compliance, analytics, everything has to integrate. A fragmented IT stack slows decision-making, increases cost, and limits your ability to pivot.
Now, let’s look at the flip side. If you get enterprise application development right, you generate serious value across the board, not just in IT, but in business performance, employee engagement, customer experience, and future-proofing. Here’s what you stand to gain:
Switching from a disconnected system to an integrated enterprise software stack, created through enterprise application development, means no more duplicate work, fewer hand-offs, and the ability to automate more processes. The result is total savings in costs, quicker execution, and decreased errors.
You will have integrated data across various departments like HR, finance, supply chain, and operations, and this will help you to create dashboards and insights. You’re not waiting for reports for days; you’re having the real-time views of what matters.
The modern enterprise application development, mobile, web, and cloud help businesses to be faster. They allow the liberalization of new territories, open new departments, and integrate systems, all without being hindered by the traditional processes of legacy systems.
Today’s employees and customers want modern mobile/web interfaces, smooth workflows, and quick access. Furthermore, the company invests in incredible enterprise mobile app development services and enterprise web app development services will keep users in a good mood and productive.
When business units talk the same language, share the same platform, you align better across the enterprise. Procurement, supply chain, HR, and finance become coordinated rather than independent domains.
By adopting modern architectures and enterprise software development services, you build not just for today but for 2026 and beyond, supporting growth, mergers, and new business models.
So, while the “problem” of fragmented systems is real, the “opportunity” of enterprise application development is arguably even more compelling.
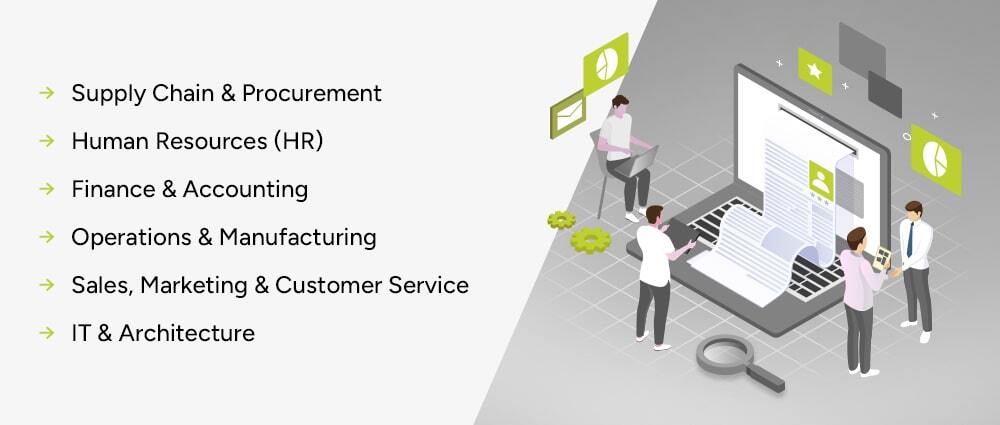
To put it simply, large enterprises means having many departments, many functions, and your application strategy needs to reflect that accordingly. Now, let us see how, together with application development, you could integrate major business functions from the very start:
Having the system where order procurement, inventory, supplier, and logistics are all tracked on one screen is like making order completion very easy. Through the development of an enterprise app or by the use of enterprise application development services, you can cut down on delays, better forecasting, optimize spending, and upgrade supplier relationships.
From recruitment to onboarding, performance management to learning, payroll to benefits, HR often sits apart. A strong enterprise app connects HR metrics to business outcomes: employee productivity, training impact, and turnover rates. You can blend HR data with business unit performance and see how talent is contributing.
Finance needs real-time visibility of expenses, procurement commitments, supplier invoices, project costs, and link that to revenue. Enterprise software development services can deliver a financial backbone tied to all other functions.
For manufacturing or operations-heavy enterprises, you want production systems, inventory, logistics, and quality control all tied into enterprise apps. One view. One workflow. One version of truth.
While sometimes seen as front-end, these functions must also integrate with the enterprise back-office. Data from customer service flows into the supply chain, marketing drives procurement in the means of promotions, and sales feedback drives operations. An enterprise approach ensures alignment.
IT is always at the forefront of every software development company. The enterprise application framework transforms into the foundation for governance, security, compliance, data architecture, and DevOps. Mobile, web, integration, cloud, and security are all included in the services for enterprise application development, thereby making IT an enabler instead of a roadblock.
Creating a unified enterprise application ecosystem means you are not only bringing all these departments to a single platform or a set of well-integrated platforms, but also to a whole integration of point solutions.
When we talk about enterprise application development, we’re really talking about a portfolio of software types, each built or integrated to serve specific business needs, but all ideally interoperable. Let’s run through the major types:
These are often built via enterprise web app development or included in enterprise software development services.
The development of enterprise applications is more than just creating new ones; it involves the integration of existing systems. Middleware, APIs, event buses, iPaaS (integration platforms) are becoming the keys for the integration.
The flow of data between departments such as HR, supply chain, and finance has to be managed properly.
Building enterprise apps isn’t a one-time affair. You’ll need continuous delivery, security, maintenance, and updates.
DevOps practices, infrastructure as code, automated testing, monitoring, and feedback loops are built into your enterprise software development services.
So, when it comes to enterprise application development in 2026, you’re not simply getting an app built; you’re building an ecosystem of systems, mobile/web front-ends, integrations, cloud infrastructure, and lifecycle practices that keep it all running smoothly.

Let’s now dissect a common scenario: you’re an enterprise looking for Enterprise Mobile App Development Services, but you also need web apps and cloud infrastructure. How do these pieces fit? What decisions should you make? Here’s the breakdown.
When employees, suppliers, partners, or customers need access via browser, you build web apps. Benefits include broad device support, ease of updates, and quick access. For large enterprises, this means building rich web portals tied to your core enterprise systems.
With your enterprise web app development services, you get:
The mobile application is the first choice of the user interface and the most effective solution when mobility, offline access, or device-specific features (camera, location, push notifications) are the major considerations. For example, such features are very useful for enterprises: field operations, sales teams, executives, and remote workers.
So, when you avail of enterprise mobile app development services, you’re looking at:
Whether your applications sit on-premise, in the cloud, or a hybrid environment, architecture is imperative. Modern enterprise application stacks make extensive use of cloud-native designs for scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. Market data, recently released, indicates that cloud deployments will take over in the case of new enterprise applications.
Thus, in your enterprise software development services, you must include:
Therefore, the workflow is as follows: you create your enterprise application ecosystem incorporating a solid backbone (cloud/integration), generate web apps that would cater to huge user groups and desktop situations, create mobile applications for the movement of people and outdoor operations, combine them all using middleware/integration, and incorporate DevOps practices to allow your system to grow.
This is enterprise application development at scale: holistic, cross-platform, strategic. The right enterprise application development services will cover all these layers and tie them back to business goals.
Okay, you know the components. Now you need a roadmap and approach. Here’s how to think about engaging enterprise software development services, selecting vendors or internal teams, and executing successfully in 2026.
What is your main goal? More effective communication between HR and supply chain? Shorter time-to-market for new business units? Anything else, just make sure your enterprise app strategy is correlated with measurable outcomes, thus you can be sure to get lower costs, better user productivity, and more satisfied customers as a result.
The same goes for enterprise application development services; you should have a very precise report: integration needs, user roles, mobile vs web, cloud vs on-premise, security/compliance requirements.
What systems do you already have? Legacy ERPs, point solutions, spreadsheets, mobile apps, maybe even disconnected islands. Map all departments and how data flows today. Identify duplication, bottlenecks, and manual hand-offs.
Use that as your baseline: you aren’t starting from scratch. The vendor or internal team offering enterprise software development services must understand your current architecture, limitations, and integrations needed.
Will you go full new build? Or a hybrid of integration and modernization? Will you use a low-code/no-code platform (gaining popularity) or custom development?
This decision influences cost, speed, flexibility, and maintainability. For large enterprises, custom still dominates, but platforms speed up development. Your enterprise mobile app development services choice may lean toward hybrid (native platform). Your enterprise web app development services may lean agile. Decide early.
Integration is a must since your company spans different fields. Consequently, the integration strategy has to cover all the mentioned aspects like APIs, data flows, identity management, real-time versus batch processing, and reporting architecture. The enterprise software development vendor you choose must be highly skilled in integration, middleware, and event-driven architecture.
If you have not yet, then it is high time you started considering a cloud or hybrid solution. The cloud will provide you with scalability, and having this kind of setup will be part of modern enterprise application development. Now, it is time to embrace microservices, containers, DevOps pipelines, CI/CD, automated testing, and monitoring. Your apps must be designed with the capacity to evolve.
Mobile should not be considered a secondary option. In 2026, mobile app development would still be held in the same regard as web app development. While using responsive design for the web, consider mobile-first or mobile-optimized design where appropriate. Utilize your enterprise mobile app development services to create apps that are very strong in performance and usability. Use your enterprise web app development services to create apps that can be accessed by a large number of users. Both should be linked with the same backend services for uniformity.
The risks involved are enormous when enterprise applications are developed. The impact of data breaches, regulatory missteps, and performance outages is severe. The developer of the enterprise application should make sure to implement all security measures like identity controls, role-based access, encryption, endpoint management (mobile devices in particular), logging and monitoring, and incident response. Furthermore, consider the compliance requirement in different locations (GDPR, local data laws).
When you roll out platform-wide enterprise apps, you’ll face change resistance. UX matters. Build interfaces that people will use, not just what you think they should use. Training, onboarding, support, and feedback loops are essential. Use analytics on usage to track adoption. This is often overlooked in enterprise software development services, but it is majorly critical.
Once launched, the job is not done. You need to monitor, update, expand, and integrate further. Use DevOps to push improvements, use analytics to find bottlenecks or underused modules, solicit user feedback, and iterate. This is the difference between just building an enterprise app and running an enterprise ecosystem for its long-term use in the organization.
Tie your investment to metrics: reduction in manual tasks, decrease in time to approve procurement, improved supplier lead time, increased employee satisfaction scores, mobile usage rates, and fewer system outages. You’ll want to justify the cost of enterprise application development services by tracking ROI.
Of course, none of this is easy. When you embark on enterprise application development (and use enterprise software development services), you will encounter hurdles. Recognizing them early helps you mitigate them.
A large enterprise usually has systems, silos, and modifications that span over several decades. The process of migrating, integrating, or replacing them is inevitably time-consuming and fraught with errors.
The expenses related to the enterprise application projects in the large-scale category can easily be summed up to a huge amount. It can be very difficult to get the different business units (procurement, HR, operations, IT) to agree on this.
Developing the application is one thing; convincing people to use it is another matter. Low adoption rates, resistance, and inadequate training diminish the value of the system.
Merging data from various systems entails the challenges of data quality, duplicates, inconsistent formats, and problems related to old data. Your analytics will be garbage-in, garbage-out if there is no proper governance.
Enterprise applications are constantly under scrutiny. With mobile apps, there is the risk of the device, while API integrations expose areas and cloud adds dependencies. It is quite a challenge to keep security intact throughout the entire system.
Performance in a system that accommodates hundreds or even thousands of users spread through various locations becomes extremely crucial. Scalability, resilience maintenance, and even failover support must be the system’s capabilities. An architectural defect may either result in very long downtime or a very bad user experience.
The selection of an inappropriate platform or a supplier may result in your being caught in a trap. In case you utilize a low-code option that binds you to a single ecosystem. If, however, the code is not written for easy maintenance, then what you have is an accumulation of technical debt.
This is the case when functions of the enterprise apps are so wide that especially aligning priorities, data definitions, workflows, and user roles is a hard task. Alignment is necessary as otherwise, you create something which does not serve the real business needs.
Cloud, mobile, microservices, AI, and IoT are among the pricipal elements that are causing the tech environment to change rapidly. Your current build must be tomorrow’s adaptable one. Too rigid a build will lead you to a rebuild sooner than expected.
Being aware of these challenges will make it easier for you to come up with mitigation plans like phased roll-outs, governance frameworks, user training programmes, architecture reviews, and vendor assessments. It is always better to bring these up now rather than after the launch.
Enterprise applications are beneficial in various sectors; nonetheless, certain industries experience a greater impact as they are managing large teams, dealing with complicated workflows, and handling huge amounts of data. Here are some industries highlighted:
Enterprise solutions are of great help to hospitals, clinics, and giant healthcare networks as they run in environments that are fast-paced and where accuracy, compliance, and timely decision-making are vitally important. Centralized patient data, automated administrative workflows, appointment management, and billing processes are some of the areas where organizations adopting enterprise healthcare solutions can see productivity gains.
Using custom healthcare software development services, providers can create tailor-made systems that promote electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine platforms, remote patient monitoring, lab integrations, and automated clinical decision support. Such solutions greatly reduce the chances of human error, facilitate better communication among different departments, and guarantee smooth coordination of care teams.
Healthcare software development services that utilize modern techniques not only help to keep the healthcare institutions regulatory compliant (like HIPAA/GDPR), but also improve the overall data security and enable the institutions to dispense personalized patient care in large quantities. In the long run, the enterprise-level application has totally changed the scenario as healthcare organizations can drastically reduce their operational burdens, make data-driven clinical decisions, and, to top it all, provide a more efficient and patient-centered experience..
The big retail companies get really good at using retail enterprise management systems that connect stock, sales, customer service and the supply chain. This enables shops to get the right amount of stock in time, to have a good shopping experience and to prevent losses.
Banks and other financial institutions resort to enterprise finance technology to manage safe transactions, customer data, regulatory compliance, and risk management. Such functions improve security, ease the processes, and also accelerate the ones that require a decision.
When it comes to logistics, delivery businesses, storage facilities, and all other departments, all depend upon enterprise logistics technology to keep track of their shipments, manage their fleets and vehicles, optimize their routes, and avoid delivery delays. This eventually results in smoother operations and, therefore, happier customers.
When you engage a provider for enterprise software development services or combine internal and external teams, you’ll want to ensure they cover several key areas. Let’s list what services you should expect and what to look for.
Clear alignment with your business goals. If they talk only tech and not business outcomes, you’ll suffer.
If you’re reading this in 2026, or even preparing for it now, there’s never been a better time to act. Projections for the global enterprise application market suggest it will grow by more than USD 295 billion by 2025, and more so, it is going to be a period of enormous digital transformations everywhere.
Digital transformation has gone through the cycle from trial to normal. There is already a shift in expectations among stakeholders who are now looking for mobile access, real-time data, and seamless workflows. Delaying your actions will only result in your losing out to competitors. The technology involved has also advanced: the trio of cloud, mobile, and microservices has now reached a level of maturity that no longer takes time, cost, or risk like never before to deliver solutions at the enterprise scale.
There has been a significant transformation in the workspace, and the enterprise systems must also portray that. Hybrid teams, mobile workers, and globally distributed businesses can only rely on applications that are user-friendly, secure, and accessible around the clock. The businesses that join in and develop interconnected app ecosystems at once will have a genuine competitive edge, expedited processes, content employees, and better flexibility.
On the contrary, those who remain connected to legacy systems are incurring costs through non-obvious ways, gradually losing their technological edge, and piling up debts in the form of outdated technology. The coming year to three years will be a period of rapid growth in AI, IoT, and edge computing. If your enterprise app stack is not prepared, then you will not only lose your position but also miss the upcoming wave of change altogether.
If you are an executive in an enterprise, an IT decision-maker, or a person spearheading digital transformation, then this is your moment to shine. The chance to create an integrated, mobile-first, web-enabled, cloud-powered enterprise ecosystem is now and it is urgent. With the proper size, the proper services, and the proper partner, you will be able to convert the idea into reality.
Arpatech plays that role. Our enterprise application development services, which include mobile, web, and software solutions, are meant to aid large businesses in uniting every department, HR, finance, supply chain, and procurement on a single, intelligent platform. We assist you in the transition from legacy systems to modern architectures that are not only faster and smarter but also easier to scale.
It’s not merely changing a few settings; it’s a complete change in the way that your business operates. The specialized teams from Arpatech will combine strategy, DevOps, and innovation to make your enterprise applications more secure, integrated, and having a long-term impact.
Creating the roadmap is easy: clarify what you want to achieve, analyze your systems, decide the best delivery model, and let Arpatech take care of the build, web, mobile, and cloud, so you can concentrate on what really matters: growth.
It’s now or never. The price of delay is very concrete: lost output, more risk, and no opportunities. But the reward? A modern enterprise application ecosystem that turns into your launchpad for expansion, innovation, and gaining an edge over competitors.
Arpatech is ready to help you build it. Let’s get started.
Enterprise application development refers to the creation of software that streamlines operations across a whole enterprise. Instead of creating an app for any particular department like HR or finance, it fuses all departments into one system. By doing so, large companies can make their operations, data, and tools neat and fruitful through controlling everything from one spot.
The making of the whole system is very difficult. There are plenty of companies that still use outdated systems which do not support modern technology. Various departments may have their unique processes, which would exacerbate the struggle of bringing the whole company onto a single platform.
Furthermore, organizations must protect their information, control who can access which part of the system, and ensure its speed for users from various locations. The application must also be scalable to accommodate the company’s growth and be compatible with the latest technologies.
To successfully tackle these difficulties, companies have to prepare well, be flexible, and utilize modern approaches such as DevOps and continuous updates. This will put their enterprise applications in a position where they are stable, secure, and prepared for the future.
A company with an extensive background in handling complicated systems, excellent technical ability, and a proven success rate is the one you should consider. Besides, they must also be familiar with your business requirements, adopt contemporary practices, and provide dependable assistance.
Arpatech is a great choice, recognized for its expertise in developing enterprise applications that are secure, scalable, and of excellent quality.
Ramsha Khan
Nov 26, 2025

Remote Patient Monitoring & Telehealth Platforms: ...
Remote patient monitoring software is becoming a strategic imperative in the healthcare industry. Health systems, clinics, telehealth companies and startups alike are asking how to develop a remote patient monitoring software that scales, that stays secure, that meets both providers and patients where they are.
Let’s dive into how you can build a remote patient monitoring software system that’s future-ready, metrics-driven and designed for scale.
First: let’s look at the numbers. The global market for remote patient monitoring is growing at a fierce pace. According to one report, the global RPM market stood at US $27.72 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach US $56.94 billion by 2030, representing a CAGR of around 12.7%.
Another puts the market at about US $22.03 billion in 2024, with expectations to reach over US $110.71 billion by 2033, or a CAGR near 19.8%. In the U.S. alone, the value of the remote patient monitoring market is forecasted to jump from about US $14.15 billion in 2024 to US $29.13 billion by 2030.
So, if your organization (or your clients) is asking: “How do we pick the best remote patient monitoring software, or become one of the remote patient monitoring software providers ourselves?”, you’re in the right place. Let’s break it down.
Before diving into architecture, you must answer some key questions:
What do we mean by “What is Remote Patient Monitoring”?
Put simply, RPM refers to technology-enabled care that collects patient data outside of traditional clinical settings (for example, in the home), transmits that data to healthcare providers, and allows interventions based on that data.
So, here are the questions you need to ask yourself before starting:
Writing this down early ensures that when developers ask “What features? What integrations? What scale?” you have metrics and business justifications.
When you ask: How to build a remote patient monitoring software, scale becomes a core consideration. Here’s what you’ll want to include:
You’ll want to connect to multiple devices (wearables, vital-sign monitors, implantables, home-health sensors). The more device types you support, the broader your market.
Support streaming, batch uploads, and offline data sync.
Ensure interoperability standards, HL7 FHIR, Bluetooth LE, WiFi, cellular, are addressed.
Use a cloud-based remote patient monitoring software architecture: it gives you automatic scale, geographic redundancy, and pay-as-you-go infrastructure.
Segment your services: device ingestion, data storage, analytics/AI, notification engine, user access (clinician and patient).
Apply multi-tenant design if you expect multiple clients or organisations, or enable healthcare cloud migration.
The volume of data is high. You’ll need logic that turns raw vital-sign data or symptom data into meaningful alerts, trends, risk scores.
AI/ML modules for predictive monitoring (for example, escalating risk of readmission) are becoming a differentiator in the market.
Medical data is sensitive. Compliance with HIPAA (USA), GDPR (EU), local health-privacy laws is mandatory. Use encrypted data-in-transit and at rest, secure device onboarding, role-based access control.
Audit logs, identity management, strong authentication.
EHR/EMR integration, telehealth platform connection (which brings us to telehealth vs RPM), billing/revenue cycle systems for remote care reimbursement.
If you’re evaluating existing options or looking to outsource a healthcare remote patient monitoring software developer, focus on these differentiators:
Can the system be customized for different care-pathways? If you need to develop a remote patient monitoring software for a niche (say renal care, post-surgery, chronic heart failure), flexibility is key.
Understand the remote patient monitoring software pricing: SaaS vs perpetual license, per-device/per-user, tiered usage.
Can the system handle thousands or millions of patients/devices?
Many clients prefer cloud-based remote patient monitoring software for ease of updates and remote management.
Providers increasingly want data on outcomes (reduced readmissions, improved adherence) to justify ROI.
The best remote patient monitoring software plays well with other systems meaning the healthcare interoperability between systems like EHRs, telehealth, and mobile apps.
Partnerships with device vendors, analytics companies, telehealth platforms strengthen your value proposition.
One common question: “What is the cost of remote patient monitoring software?” Cost is multi-factorial: number of patients/devices, complexity of workflows, integrations, regulatory compliance, customizations, hosting model, IT support, maintenance.
According to our expert opiion:
There’s no one-size-fits-all “price list” for “software for remote patient monitoring” or “remote patient monitoring software system” given the variations. That’s why building modular and scalable is key, it allows costs to scale more predictably.
Because, let’s be honest: technology is useful, but adoption is critical. A high-performing system means nothing if clinicians and patients don’t use it. Some tactics:
When you think of building a scalable RPM system, you’ll frequently hear the term “telehealth platforms” alongside it. While closely connected, they serve different roles. We’ll look at the difference below, but for now understand: a robust remote patient monitoring software development project will integrate seamlessly with telehealth to provide a full-care experience: data collection + virtual consultation + intervention.
Since you’re building something scalable and transactional, you’ll want to monitor these KPIs:
When you’re discussing a project or prospect for best remote patient monitoring software, these metrics help demonstrate ROI and scalability.
If you are contemplating to become a provider or choosing one that offers remote patient monitoring software, the first thing to consider is: the market is full of sellers, so it is vital to differentiate yourself:
When you mention “remote patient monitoring software providers,” these are the features that make you different from the rest.
Here are some practical tips gleaned from real-world cases:
Select a small cohort of patients, monitor data flows, clinician engagement, patient behaviour.
Patients hate complicated device set-ups. Use plug-and-play as much as possible.
New dashboards can disrupt workflows; invest in change management.
Build your compliance, privacy, consent systems from day one. Retrofitting is expensive.
Auto scaling, auto updates, logging/monitoring.
Show them trends and outcomes (not just raw device data) and build for localization and different regulatory regimes if you will scale globally.
Remote monitoring and telehealth technologies evolve fast; you want a modular code base.
Without sufficient patient engagement, your system won’t deliver value.
Device vendors, telehealth vendors, and analytics vendors often form ecosystems; join them rather than reinvent everything.
If your organization is ready to step into this space, to build a remote patient monitoring software or upgrade an existing platform, now is an excellent time. With a growing global market, increasing demand from chronic-disease care and home-care models, and telehealth becoming mainstream, your opportunity is large.
At Arpatech, we specialise in remote patient monitoring software development and can help you every step of the way: from concept and architecture to deployment and scaling. Whether you’re looking to develop a remote patient monitoring software from scratch or integrate enhanced features into an existing system, we can guide you through technology choices, cloud-based deployment, regulatory compliance, and user adoption.
Let’s build your next-generation remote patient monitoring platform together, one that delivers outcomes, scales effortlessly, and positions you as a leader among remote patient monitoring software providers.
There is no single answer, because cost depends on number of patients/devices, feature scope, integrations, regulatory complexity, deployment model (cloud vs on-premises). As noted above, for a full custom build, you might expect budgets to be on a little higher side.
On a per-patient SaaS basis, some packaged solutions may charge hundreds of dollars per patient per year. The key is to define the scope clearly and build modularly so you can add features as you scale.
Yes, from both a care-delivery and business perspective. The data shows strong growth in uptake and market size, and the ability to monitor patients outside the hospital enables lower costs, better outcomes (reduced readmissions, earlier interventions), greater patient reach.
If implemented well (with good UX, clinician buy-in, patient adherence), remote patient monitoring can provide a real competitive advantage and cost savings.
In short: telehealth is a broader umbrella term covering virtual visits, tele-consultations, remote delivery of healthcare services via audio/video. Remote patient monitoring is a subset focused on monitoring patient health data remotely (such as vital signs, device data, symptoms) outside a traditional clinical setting, and acting on insights from that data.
They work together: RPM collects the data, telehealth enables the intervention. But they are distinct in terms of workflow, requirements and technology.
Ramsha Khan
Oct 30, 2025

Edge + IoT in Smart Hospitals: Architectures for Real-T...
Hospitals are no longer just buildings with beds and corridors; they’re becoming data centers on the move. Between bedside monitors, wearable sensors, smart IV pumps, imaging devices and building systems, modern hospitals produce massive amounts of data every second. To turn that stream into immediate, actionable care we need computing where the data is born, not 1,000 miles away in a cloud datacenter. That’s where edge computing in healthcare and IoT architectures for smart hospitals step in: processing, analyzing and acting on data at the bedside or inside the hospital network for true real-time healthcare.
Today, we’ll explain practical architectures, real edge computing applications in healthcare, high-impact use cases, measurable benefits, and best practices you can adopt today, all in plain language and with two solid industry stats to anchor the case.
Imagine a cardiac telemetry monitor that detects a dangerous arrhythmia. If that monitor must send raw waveform data to a distant cloud, wait for analysis, then return an alert, valuable seconds, or minutes, are lost. Edge nodes (local servers, gateways, or even smart devices) analyze the waveform immediately, surface the alert to clinicians, and optionally send a summarized record to the cloud for archival and analytics.
That drop in latency and the ability to filter and pre-process large data streams is why Edge Computing Transformation in Healthcare is more than a buzzword; it’s a practical shift that enables real-time decisions in critical care. Edge also reduces bandwidth and lowers the exposure of sensitive data in transit, improving privacy and compliance.
A reliable smart-hospital architecture usually layers computing so each task runs where it makes most sense:

This hybrid lets you run immediate detection and automation at the edge while keeping the cloud for heavy lifting, historical analytics and cross-site intelligence.
Edge computing in healthcare unlocks a range of practical, high-value applications:
These edge computing applications in healthcare reduce noise, surface the right events, and free clinicians to act faster with higher confidence.
Market growth: Analysts estimate the edge computing in healthcare market will grow substantially, from roughly USD 6.18 billion in 2024 to about USD 38.12 billion by 2032, driven by demand for low-latency processing and real-time care use cases. This creates strong commercial incentive to adopt edge architectures.
Performance impact: Research comparing edge-enabled clinical systems shows dramatic latency and network improvements, in one study, moving analytics to the edge produced an average latency reduction of about 87.7× and improved overall network efficiency (bandwidth) by roughly 2.6×, results that matter a lot in critical workflows.
Use cases like real-time arrhythmia detection or surgical-assistance AI become possible when inference runs locally with those kinds of performance gains.
When evaluating whether to adopt an edge + IoT model, hospitals repeatedly cite a set of powerful advantages that improve clinical outcomes, operational reliability, and cost efficiency. Let’s look at each benefit in detail.
In the healthcare field, every second matters and can be the difference between saving a life or not. By utilizing IoT and edge computing in healthcare, the data of patients coming from monitors, imaging devices, or wearables is being processed right where it’s collected instead of being sent to a faraway cloud for analysis. This has the effect of cutting down latency and thus, it is almost instant that doctors and nurses get notified, patients are updated, and diagnostic results are available.
To illustrate, when the oxygen saturation of a patient drops suddenly, the edge-based monitoring system will not just sit there and wait for cloud confirmation but will instead send an alert to the medical team right away. This rapidity allows for drug adjustments, interventions, and directed responses, especially in emergency rooms, ICUs, and operating theaters, among others, to be done faster and to save lives.
Every minute, hospitals are creating huge data volumes ranging from medical imaging to IoT sensors and smart devices. All these unprocessed data are transferred to the cloud may push the network capacity to its limits and cause an increase in operational costs.
On the other hand, with edge computing, only the summaries, insights, and flagged anomalies are being sent to the cloud for storage, while the raw data is being processed and filtered right where it is produced. This scenario lessens the strain on hospital networks, cuts down on the use of bandwidth, and gives the IT teams an opportunity to manage the data more efficiently. In other words, the edge allows hospitals to smartly deal with the “data noise”, that is keeping the useful part and throwing away the rest.
Every healthcare institution puts the safeguarding of patient information as their main priority. The adoption of edge computing in the healthcare sector elevates the level of data security because it enables the processing of sensitive patient data at the local hospital, or at least very close to the point of care.
This type of processing means that the personal health information (PHI) will not undergo long travels across the internet to the remote data centers, hence the risk of interception or breaches is significantly decreased. Furthermore, it makes it easier to adhere to the strict regional data protection regulations, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or any local health data law. By ensuring that the sensitive data remains within the controlled perimeter, hospitals obtain the dual benefit of enhanced privacy and seamless compliance.
Hospitals cannot afford downtime, even a short network interruption can disrupt care delivery. Edge computing in healthcare ensures continuous operation by processing data locally, independent of external internet connectivity.
So even if the hospital’s connection to the cloud is temporarily lost, critical systems, like patient monitors, medication pumps, or diagnostic devices, continue functioning seamlessly. This built-in resiliency guarantees uninterrupted service and patient safety, making edge computing a cornerstone of high-availability healthcare IT infrastructure.
Running every application and storing every piece of data in the cloud can become expensive over time, especially with continuous data streaming from thousands of devices. By adopting an edge architecture, hospitals reduce cloud egress, bandwidth, and storage costs, since most processing and filtering happen locally.
Moreover, edge computing allows for targeted investments, hospitals can deploy high-performance edge nodes only where they’re needed most (like ICUs or surgical departments) rather than scaling cloud capacity across all systems. The result? Lower operational costs, better resource allocation, and a strong long-term ROI for healthcare organizations.
Put simply, edge computing transforms constant device chatter into meaningful, actionable insights. Instead of drowning in unfiltered data, hospitals can focus on what truly matters, faster responses, better care, and smarter decisions. With the right strategy, edge + IoT technologies make healthcare not just more connected, but also more intelligent and human-centered.
If you’re designing Edge computing applications in healthcare or planning pilots, use these practical best practices:
These are the Best practices for edge computing in healthcare that teams with successful deployments follow.
The Future of Computing in Healthcare looks hybrid and distributed. Expect:
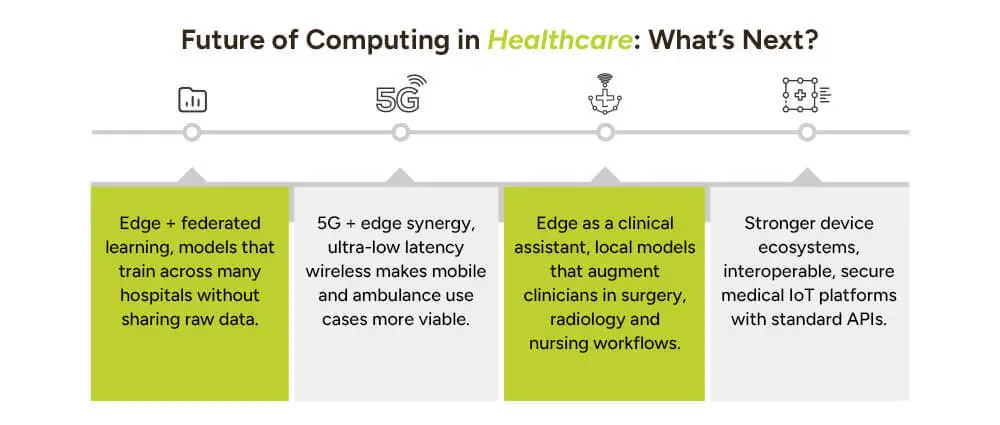
The future is less about cloud vs. edge and more about using each layer where it delivers the most clinical and operational value.
At Arpatech, we empower hospitals and healthcare providers to build intelligent, secure, and compliant edge-to-cloud ecosystems. Our team specializes in:
Whether you’re upgrading existing hospital systems or launching a smart healthcare initiative from the ground up, Arpatech Cloud provides the technical backbone and strategic expertise to make it happen faster, safer, and smarter.
Transform your healthcare infrastructure today.
Short answer: Cloud computing centralizes heavy processing, storage, and long-term analytics in remote datacenters; edge computing moves processing closer to the devices (bedside, gateway, or hospital server) so time-sensitive tasks run locally.
In practice: use the edge for real-time inference, immediate alarms, privacy-sensitive preprocessing, and to keep services running during network outages. Use the cloud for migration, training models, population-level analytics, archival storage, and cross-facility reporting. A hybrid approach, edge for speed and privacy, cloud for scale and longitudinal intelligence, is the recommended pattern for modern smart hospitals.
Ramsha Khan
Oct 28, 2025

Healthcare Mobile App Development: From Idea to Launch
Healthcare is no longer confined to hospitals and clinics; with the tech-driven landscape of today, combined with remote care, you can have everything at home. With just a few taps on your phone, you can schedule appointments, access your medical records, or even speak to a doctor, thanks to healthcare mobile app development.
Whether you’re a startup founder, a hospital admin, or someone with a brilliant idea to revolutionize care delivery, this blog is your go-to healthcare mobile app development guide. From turning your idea into a fully functional app to choosing the right partner, we’re covering it all, step by step.
Let’s start with the basics.
A healthcare mobile app is any application that helps patients or healthcare providers manage health-related tasks on mobile devices. These apps can do a variety of things, like:
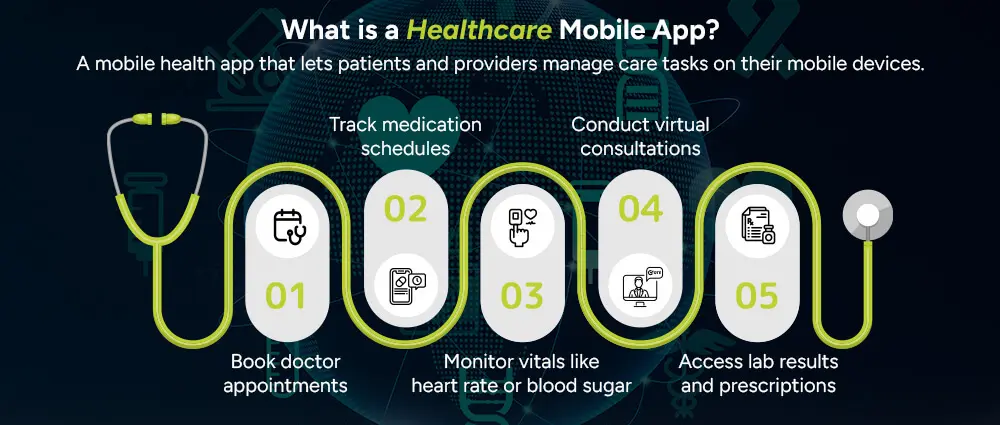
In short, they put essential healthcare services right in your pocket.
According to Deloitte, healthcare is rapidly moving toward modern technology. Around 60% of providers now see platforms like EMRs and ERP systems as essential for their long-term operations, and nearly 90% of executives believe digital transformation will accelerate even further in
Mobile app development for health care is mainly focused on making care uncomplicated and hassle-free for all.
Generally, the benefits that each party takes away are:
So, we can say that mobile app development in healthcare is transforming the way patients and providers interact, making medical services more accessible, efficient, and personalized. From enabling remote consultations and real-time health tracking for patients to reducing administrative tasks and offering valuable data insights for providers, these apps are revolutionizing care delivery. As technology continues to advance, mobile healthcare solutions will only grow more essential in creating a connected, responsive, and inclusive healthcare ecosystem.

Building a mobile healthcare app development project from scratch can sound daunting, but breaking it down helps. Here’s your roadmap when it comes to mobile app ideas for 2025 for all industries, especially healthcare:
Is your app solving a real problem? Talk to doctors, nurses, patients, and insurers for real insights. Research competitors. Know what makes your idea different.
Start by identifying the exact healthcare problem your app will solve. Study the current market to see what solutions already exist and how yours stands out. Validation ensures you’re building something people actually need and will use, whether you need a mobile app for SMBs or any large enterprise.
Don’t overload your first version. Focus on the must-haves, avoid including everything in the first version, and prioritize what users value most:
We can focus on detailed features later on, but first and foremost, you need the structure of your application.
Healthcare apps deal with sensitive personal data, compliance isn’t something that you can take as an optional thing. Make sure your app follows healthcare laws like:
This step is critical when building trust and ensuring patient data safety. Being compliant also builds trust, keeps you legally and ethically protected, and these laws also regulate how health data is stored and shared.
Simplicity is key. Healthcare users are often not tech experts. Make sure your app is intuitive, clean, and accessible because Healthcare users span all ages and tech comfort levels. Use clean layouts, large buttons, and clear navigation for easy interaction.
Decide whether you’re going for native stack for iOS, Android or a cross-platform app framework like Flutter, React Native. This impacts cost, time, and performance.
But what do you need to look for? Select technologies based on your goals, timeline, and budget. When it comes to cross-platform tools like Flutter or React Native, reduce cost and time. Don’t forget backend technologies and integrations with EHR or cloud platforms.
Working with a reliable healthcare mobile app development company ensures your app is secure, scalable, and built with industry best practices. Make sure that the healthcare mobile app development service you collaborate with brings technical expertise and knowledge of industry standards and risks. With a good partner, you can ensure that the app is secure, scalable, and easy to maintain. You can develop your healthcare mobile app with Arpatech, a team trusted by businesses worldwide for end-to-end development.
Before the launch, test everything: functionality, security, speed, and user experience. Include healthcare professionals in your beta testing phase.
Testing isn’t just about fixing bugs; it ensures patient safety and reliability. You should make sure that the company runs usability tests, security audits, and stress tests across devices. This phase is used to refine workflows and fix any potential friction points.
Launch your MVP, gather feedback from real users, and keep iterating. Healthcare is always evolving, so your app should too.
Monitor performance, crash reports, and user behavior analytics post-launch. Iterate quickly, release improvements and new features in regular updates. We just need to remember that the healthcare landscape is dynamic, and all apps must evolve with it.
Many businesses like ecommerce are now using AI apps to give out a more appealing look to their audience. Depending on your app’s goals like doctor-patient interaction, wellness tracking, hospital admin, etc., here are some key features to consider:
The right set of features depends on your users, goals, and region.
Choosing a development partner is just as important as the app idea itself.
Here’s what to look for in a healthcare mobile app development company:
If you’re looking for all of the above, develop your healthcare mobile app with Arpatech. We’ve helped startups and hospitals bring impactful healthtech ideas to life.
At Arpatech, our healthcare and fintech mobile app development services are built around your unique needs. Whether it’s a patient engagement platform, an EMR app, a telehealth solution or adding the benefits of AI in mobile app development, we handle:
Let’s turn your idea into an app that makes a real difference.
Healthcare mobile app development is more than just coding; it’s about creating tools that can improve lives. Whether you’re starting from scratch or upgrading an existing system, partnering with the right experts makes all the difference.
From ideation to deployment, we understand the nuances of healthcare technology. So, if you’re wondering how to build a healthcare app or looking for trusted mobile app development healthcare professionals, develop your healthcare mobile app and software with Arpatech, we’ve got you covered.
Let’s build something that matters, for you, your users, and the future of care
It depends on the complexity, features, platform (iOS/Android/both), and whether it’s HIPAA-compliant. On average, the cost of healthcare mobile app development can vary from thousands to a few million dollars, all depending on the complexity and technology stack. A basic MVP might be on the lower end, while full-scale apps with advanced features can go higher.
Again, it depends on your scope. A simple MVP may take 3–5 months, while a feature-rich app could take 6–12 months or more. Including testing and compliance adds to the timeline but is well worth the effort.
Mobile app development in healthcare are used for:
If we go more into the niche of things and work our way into every department in the healthcare industry, we can look for and bring advancement to each department, thus creating more apps to work with in the future and bringing automation in every aspect of care.
Ramsha Khan
Oct 24, 2025